Zusammenfassung
Summary Bio-Imaging
- Kurs
- Hochschule
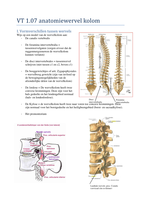
A 25 page summary of the entire course based on the slides from the lectures and the course notes (booklet)
[ Mehr anzeigen ]vorschau 2 aus 25 Seiten
Vorschau 2 aus 25 Seiten

Stuvia Verkäufer haben mehr als 700.000 Zusammenfassungen beurteilt. Deshalb weißt du dass du das beste Dokument kaufst.

Man bezahlt schnell und einfach mit iDeal, Kreditkarte oder Stuvia-Kredit für die Zusammenfassungen. Man braucht keine Mitgliedschaft.

Deine Mitstudenten schreiben die Zusammenfassungen. Deshalb enthalten die Zusammenfassungen immer aktuelle, zuverlässige und up-to-date Informationen. Damit kommst du schnell zum Kern der Sache.
Du erhältst eine PDF-Datei, die sofort nach dem Kauf verfügbar ist. Das gekaufte Dokument ist jederzeit, überall und unbegrenzt über dein Profil zugänglich.
Unsere Zufriedenheitsgarantie sorgt dafür, dass du immer eine Lernunterlage findest, die zu dir passt. Du füllst ein Formular aus und unser Kundendienstteam kümmert sich um den Rest.
Stuvia ist ein Marktplatz, du kaufst dieses Dokument also nicht von uns, sondern vom Verkäufer CVSTICHE. Stuvia erleichtert die Zahlung an den Verkäufer.
Nein, du kaufst diese Zusammenfassung nur für 7,49 €. Du bist nach deinem Kauf an nichts gebunden.
4.6 Sterne auf Google & Trustpilot (+1000 reviews)
45.681 Zusammenfassungen wurden in den letzten 30 Tagen verkauft
Gegründet 2010, seit 15 Jahren die erste Adresse für Zusammenfassungen