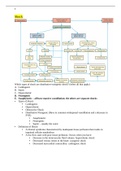
College aantekeningen
University Physics - Linear Dynamics
- Vak
- Instelling
- Boek
This is the first part of the course that covers topics ranging from Displacement & Velocity in 1D, Vectors & 2D Kinematics, Relative & Circular Motion, Newton's Laws, Forces & Free-Body Diagrams, and Friction.
[Meer zien]