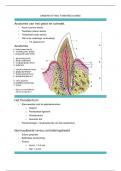
Resumen
Summary Unit/Module 2 - Cells
- Grado
- Institución
Whole of Unit/Module 2, Cells for AQA A level Biology based on class notes, specification, textbooks, websites, videos and revision sessions. Summarised into bullet point notes that are quick and to the point with just information you need for the exam.
[Mostrar más]