Molecular biology
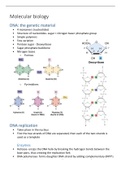
DNA: the genetic material
• 4 monomers (nucleotides)
• Structure of nucleotides- sugar + nitrogen base+ phosphate group
• Simple polymers
• Few variation
• Pentose sugar - Deoxyribose
• Sugar-phosphate backbone
• Nitrogen bases
○ Purines
○ Pyrimidines
DNA replication
• Takes place in the nucleus
• First the two strands of DNA are separated, then each of the two strands is
used as a template
Enzymes
• Helicase- unzips the DNA helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the
base pairs, thus creating the replication fork
• DNA polymerase- forms daughter DNA strand by adding complementary dNTP's
to 3' end. Cannot initiate new strand formation, cannot start from scratch.
• Polymerase III- proofreading, adds dNTP's
• Polymerase I- replaces RNA primers with DNA
, • Helicase- unzips the DNA helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the
base pairs, thus creating the replication fork
• DNA polymerase- forms daughter DNA strand by adding complementary dNTP's
to 3' end. Cannot initiate new strand formation, cannot start from scratch.
• Polymerase III- proofreading, adds dNTP's
• Polymerase I- replaces RNA primers with DNA
• RNA primase- forms RNA primer, which acts as a guide for polymerase. The
primer is later removed and dNTP's are added
• DNA ligase- joining together the Okazaki fragments on lagging strand
• Topoisomerase- keeps the helix and the templates from supercoiling
Process
• The helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs, thus creating
the replication fork, multiple helicases are needed on different segments of
DNA, which are called sites of origin => multiple replication
• Helicase is unzipping from 3' to 5' direction
○ Since helicase unzips from 3' to 5', and DNA pol II ads only to 3', the
replication is continuous -> leading strand
○ The opposite strand, helicase again unzips from 3' to 5', and DNA pol II
ads only to 3' on the new strand, the replication is done in small parts
called the Okazaki fragments and the strand is called lagging strand -
discontinuous
• RNA primase makes a short RNA strand called a primer whish shows DNA pol
where to start.
• DNA pol III adds dNTP's to the 3' end of the primer.
• DNA pol I removes the short segments of RNA primers, changed by the
complementary dNTP's
• DNA ligase joins/ seals DNA Okazaki fragments, producing one continuous
strand again 3' to 5'
Bidirectional replication in E.coli
Theta replication
DNA: the genetic material
• 4 monomers (nucleotides)
• Structure of nucleotides- sugar + nitrogen base+ phosphate group
• Simple polymers
• Few variation
• Pentose sugar - Deoxyribose
• Sugar-phosphate backbone
• Nitrogen bases
○ Purines
○ Pyrimidines
DNA replication
• Takes place in the nucleus
• First the two strands of DNA are separated, then each of the two strands is
used as a template
Enzymes
• Helicase- unzips the DNA helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the
base pairs, thus creating the replication fork
• DNA polymerase- forms daughter DNA strand by adding complementary dNTP's
to 3' end. Cannot initiate new strand formation, cannot start from scratch.
• Polymerase III- proofreading, adds dNTP's
• Polymerase I- replaces RNA primers with DNA
, • Helicase- unzips the DNA helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the
base pairs, thus creating the replication fork
• DNA polymerase- forms daughter DNA strand by adding complementary dNTP's
to 3' end. Cannot initiate new strand formation, cannot start from scratch.
• Polymerase III- proofreading, adds dNTP's
• Polymerase I- replaces RNA primers with DNA
• RNA primase- forms RNA primer, which acts as a guide for polymerase. The
primer is later removed and dNTP's are added
• DNA ligase- joining together the Okazaki fragments on lagging strand
• Topoisomerase- keeps the helix and the templates from supercoiling
Process
• The helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs, thus creating
the replication fork, multiple helicases are needed on different segments of
DNA, which are called sites of origin => multiple replication
• Helicase is unzipping from 3' to 5' direction
○ Since helicase unzips from 3' to 5', and DNA pol II ads only to 3', the
replication is continuous -> leading strand
○ The opposite strand, helicase again unzips from 3' to 5', and DNA pol II
ads only to 3' on the new strand, the replication is done in small parts
called the Okazaki fragments and the strand is called lagging strand -
discontinuous
• RNA primase makes a short RNA strand called a primer whish shows DNA pol
where to start.
• DNA pol III adds dNTP's to the 3' end of the primer.
• DNA pol I removes the short segments of RNA primers, changed by the
complementary dNTP's
• DNA ligase joins/ seals DNA Okazaki fragments, producing one continuous
strand again 3' to 5'
Bidirectional replication in E.coli
Theta replication