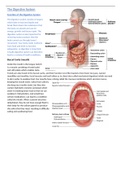
Function of the Digestive System
The digestive system consists of organs
which take in food and liquids and
break them down into substances that
the body can absorb and use for
energy, growth and tissue repair. The
digestive system is also important for
removing waste products that the
body cannot use through bowel
movement. Your body needs nutrients
from food and drink to function
adequately, so digestion is important.
A faulty digestive system can therefore
lead to a variety of health conditions.
Buccal Cavity (mouth)
Inside the mouth is the tongue (which
is a muscle consisting of taste buds)
and soft palate which enables taste.
Tonsils are also found in the buccal cavity, and their function is to filter bacteria from food. Our jaws, named
mandibles and maxillae, facial muscles and teeth allow us to chew (also called mechanical digestion) which we need
to do in order to swallow food. Our mouths have a lining called the mucous membrane which secretes mucus,
keeping the mouth moist. Saliva from salivary
also keep our mouths moist, but they also
contain hydrolytic enzymes (amylase) which
assist in breaking down food so that we can
swallow it. Dehydration, and sometimes
certain medications, can lead to a condition
called dry mouth. When a person becomes
dehydrated, they do not have enough fluid in
their body for the salivary glands to produce
the saliva that they need, resulting in difficulty
eating and swallowing food.
,Pharynx
The pharynx is a cavity lined with muscle situated at the back
of the throat. A person’s tongue rolls chewed up contents
(food) into a ball (often called a bolus). The tongue then
proceeds to push it up against the roof of the mouth, where
both the hard and soft palates are situated, to the pharynx
where the process of swallowing occurs. Swallowing is an
involuntary reflex which means that we do not have to
consciously control our muscles when we are swallowing. The
muscles located in the pharynx begin to contract and the
tongue pushes up against the roof of the mouth, closing off
the airway. Health conditions including strokes, head injuries,
multiple sclerosis and dementia, cancer (mouth or
oesophageal) or gastro-oesophageal reflex disease may cause
dysphagia which is the medical term for swallowing
difficulties. Symptoms of dysphagia include coughing or
choking when consuming substances, bringing food back up, persistent drooling of saliva or inability to properly
chew food. Treatments include speech therapy to learn new swallowing techniques, altering the consistency of
food/liquids to make them easier to swallow, alternative forms of consuming such as tube feeding through the nose
or stomach or surgery to widen the oesophagus by stretching it or inserting a stent.
Oesophagus
The oesophagus is a muscular tube which is around 25cm long with a diameter of 2.5cm. The walls
of the oesophagus include 4 layers, including a mucous membrane which moistens the oesophagus by
secreting mucus, ensuring a smooth and easy passage of food. The submucosa present keeps the
mucous membrane in its position, a dense layer of muscle consisting of smooth muscle fibres
which are circular and longitudinal, and a protective covering on the exterior. The
oesophagus pushes food into the stomach by peristalsis. Sometimes the muscles in the
oesophagus can fail to contract properly, making it difficult for food and liquids to be pushed
down into the stomach. This condition is called oesophageal motility, one type of which is called
achalasia. This condition is when the nerves in the oesophagus deteriorate, resulting in the
muscles failing to work properly and causing the valve at the bottom of the oesophagus to not
open. Studies have shown that achalasia may be caused by an immune disorder, in which the
patient’s own immune system attacks their nervous system. This condition causes difficulty
swallowing and sometimes regurgitation. Although there is no cure for achalasia, various
medications and surgical procedures may be performed to help treat the symptoms.
Stomach
The stomach is a bag like structure made of muscle located in the
upper part of the abdomen, sitting under the diaphragm. Its
walls consist of a thick muscular layer, consisting of smooth
muscle fibres that are longitudinal, circular and oblique and lined
with epithelial cells. Food reaches the stomach when the
oesophagus pushes it down into the stomach. Epithelial cells in
the stomach produce gastric juice that contains hydrochloric acid
and enzymes. The muscular wall of stomach creates peristaltic
movement which churns the food and mixes it with enzymes to
make chyme. Sometimes the nerves which are responsible for
controlling how the stomach empties become damaged which
results in the muscles of the stomach not working properly and
thus slowing down the movement of food. This condition is
called gastroparesis, and some known causes of this condition
, are poorly controlled type 1 and type 2 diabetes and a complication of surgeries such as weight-loss surgery or a
gastrectomy (removal of part of the stomach). There is no cure for gastroparesis, however, dietary changes and
medical treatment usually help control the condition.
Small Intestine (Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum)
Nutrients are absorbed by the small intestine. Nutrients are absorbed by receiving pancreatic juice and bile from the
liver which are needed for the small intestine to function. The small intestine includes the duodenum, the jejunum
and the ileum, which are all vital for the products of digestion to be absorbed.
At the pyloric end of the stomach the chyme’s
acidity causes relaxation of the pyloric sphincter
muscle. Chyme is able to pass into the duodenum
but only in small quantities.
The duodenum has a total length of around 25cm.
The diameter of the duodenum is 2.5cm. It is
attached to the dorsal abdominal wall. The
duodenum is made up of layers of epithelium-lined
smooth muscle cells. The duodenum is where
absorption normally starts. The duodenum collects
pancreatic juice that does include hydrolytic
enzymes. As well as this, the duodenum receives
bile from the liver. In the area called the sphincter
of Oddi, these secretions reach the duodenum.
With a diameter of around 3.8cm, the jejunum is
about 3.6m in length. It stretches from the
duodenum to the ileum. Jejunum absorbs fatty
acids, amino acids and sugars.
The length of the ileum is 3.6m. The walls of the
Ileum are smoother, thinner and more heavily folded than the walls of the Jejunum. There are villi in the epithelium,
which are finger-like projections. Such properties help increase the ileum's surface area for the absorption of
digestion materials. On a membrane called the Mesentery, both the jejunum and the ileum are supported. Any
nutrients that have not been absorbed by the duodenum or jejunum are absorbed by the ileum.
Poor absorption of nutrients at any section of the small intestine can result in short bowel syndrome. This condition
is a result of the small intestine not absorbing enough vitamins, water and various other nutrients from consumed
food. The most common symptom of short bowel syndrome is diarrhoea which can cause dehydration, malnutrition
and weight-loss. If left untreated, this condition can lead to death. However, treatments such as rehydration
solutions and medications are available. In some cases, patients may be able to receive an intestinal transplant.
Pancreas
The pancreas is a gland, and it is supported by a membrane called the mesentery. The pancreas is situated within the
loop of the duodenum. It produces a variety of hydrolytic enzymes to enable digestion of all the various food types.