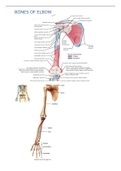
BONES OF ELBOW
, Consists of humerus, ulnar & radius
Joints: shoulder & elbow
HUMERUS
Surgical neck → usually refers to the most commonly fractured region
o Also area where axillary nerve most likely to be injured
Anatomical neck → based on centres of ossification, capsular ligament insertion of shoulder
joint
ORIF → open reduction and internal fixation
Nutrient foramen → entrance in all bones for blood vessels
o Especially in shafts of larger long bones
o Foramina lead to nutrient canal & can extend into medullary cavity of bone
Muscle origins & insertions
, ELBOW
Olecranon fossa receives olecranon during forearm extension
Coronoid fossa articulates with coronoid process of ulna
Condyle(capitulum & trochlea) → a rounded protuberance at the end of some bones,
forming an articulation with another bone
Synovial joint → made up of joint between trochlear notch and trochlea; the capitulum and
head of radius
o Diarthoses - free movable joint
o Articular bone surfaces are separated by hyaline cartilage layer
o Synovial fluid allows smooth movement
o Joint enclosed by fibrous capsule (internally lined by synovial membrane)
Movement at elbow joint include flexion and extension(mono-axial)
movement at elbow complex
o Pronation & supination of forearm
o Pivot joint at radio-ulnar joint
Anterior view
, Consists of humerus, ulnar & radius
Joints: shoulder & elbow
HUMERUS
Surgical neck → usually refers to the most commonly fractured region
o Also area where axillary nerve most likely to be injured
Anatomical neck → based on centres of ossification, capsular ligament insertion of shoulder
joint
ORIF → open reduction and internal fixation
Nutrient foramen → entrance in all bones for blood vessels
o Especially in shafts of larger long bones
o Foramina lead to nutrient canal & can extend into medullary cavity of bone
Muscle origins & insertions
, ELBOW
Olecranon fossa receives olecranon during forearm extension
Coronoid fossa articulates with coronoid process of ulna
Condyle(capitulum & trochlea) → a rounded protuberance at the end of some bones,
forming an articulation with another bone
Synovial joint → made up of joint between trochlear notch and trochlea; the capitulum and
head of radius
o Diarthoses - free movable joint
o Articular bone surfaces are separated by hyaline cartilage layer
o Synovial fluid allows smooth movement
o Joint enclosed by fibrous capsule (internally lined by synovial membrane)
Movement at elbow joint include flexion and extension(mono-axial)
movement at elbow complex
o Pronation & supination of forearm
o Pivot joint at radio-ulnar joint
Anterior view