Summary
Summary transport across cell membranes
- Course
- Institution
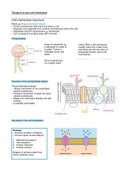
Summary notes for AQA A-level Biology Transport across membranes. Includes clear information on cell membrane structure, transport processes (osmosis, active transport, co-transport, diffusion). Summarised from class notes and the official course textbook. From an A* student.
[Show more]