Tentamen (uitwerkingen)
PYC1501_Basic Psychology.
- Vak
- Instelling
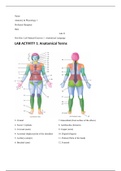
PYC1501_Basic Psychology A-Z: Information modeling: Flow Charts • A FLOW CHART is a diagram that shows a flow or stream of information belonging to a central theme. • The chart should be well-formed, valid, relevant and comprehensive. • A well-formed chart: o The elements of the ch...
[Meer zien]