Summary
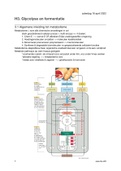
Samenvatting Hoofdstuk 3 Glycolyse en fermentatie Johan Van Lint metabolisme en metabole regeling
- Course
- Institution
Dit is de samenvatting van Hoofdstuk 3 Glycolyse en fermentatie Johan Van Lint uit Metabolisme en metabole regeling.
[Show more]