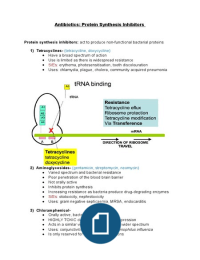
Antibiotics: Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Protein synthesis inhibitors: act to produce non-functional bacterial proteins
1) Tetracyclines- (tetracycline, doxycycline)
Have a broad spectrum of action
Use is limited as there is widespread resistance
S/Es: erythema, photosensitisation, tooth discolouration
Uses: chlamydia, plague, cholera, community acquired pneumonia
2) Aminoglycosides- (gentamicin, streptomycin, neomycin)
Varied spectrum and bacterial resistance
Poor penetration of the blood brain barrier
Not orally active
Inhibits protein synthesis
Increasing resistance as bacteria produce drug-degrading enzymes
S/Es: ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity
Uses: gram negative septicaemia, MRSA, endocarditis
3) Chloramphenicol-
Orally active, bacteriostatic drug
HIGHLY TOXIC due to bone marrow suppression
Acts in a similar way to erythromycin but wider spectrum
Uses: conjunctivitis, meningitis and Haemophilus influenza
Is only reserved for very serious infections
, 4) Macrolides- (erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin)
Similar range of action and efficacy to penicillins
Suitable alternative for penicillin sensitive individuals
Can cause diarrhoea and jaundice
Uses: respiratory infection, otitis media, H. pylori, bronchitis, pertussis
Protein synthesis inhibitors: act to produce non-functional bacterial proteins
1) Tetracyclines- (tetracycline, doxycycline)
Have a broad spectrum of action
Use is limited as there is widespread resistance
S/Es: erythema, photosensitisation, tooth discolouration
Uses: chlamydia, plague, cholera, community acquired pneumonia
2) Aminoglycosides- (gentamicin, streptomycin, neomycin)
Varied spectrum and bacterial resistance
Poor penetration of the blood brain barrier
Not orally active
Inhibits protein synthesis
Increasing resistance as bacteria produce drug-degrading enzymes
S/Es: ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity
Uses: gram negative septicaemia, MRSA, endocarditis
3) Chloramphenicol-
Orally active, bacteriostatic drug
HIGHLY TOXIC due to bone marrow suppression
Acts in a similar way to erythromycin but wider spectrum
Uses: conjunctivitis, meningitis and Haemophilus influenza
Is only reserved for very serious infections
, 4) Macrolides- (erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin)
Similar range of action and efficacy to penicillins
Suitable alternative for penicillin sensitive individuals
Can cause diarrhoea and jaundice
Uses: respiratory infection, otitis media, H. pylori, bronchitis, pertussis