Biologische psychologie: HT7: gehoor, evenwicht, tast, smaak en
geur
GEHOOR
1. De stimulus: geluid
* trillende objecten doen luchtmoleculen bewegen
* veroorzaken luchtdrukverschillen = luchtdrukgolven (afwisseling
compressie/ijle lucht)
* waarneembaar voor mensen: frequentie tss 30-20.000/sec
(Hz)
* frequentie = toonhoogte
* amplitude = volume
* mengeling/boventonen = timbre
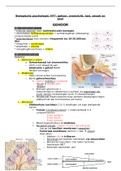
2. Anatomie v/h oor
Opdeling:
Buitenoor = pinna
o Gehoorkanaal tot trommelvlies
o Vorm v oor draagt bij aan
lokalisatie v geluid MAAR
flexibel vermogen
Middenoor
o Holle ruimte achter trommelvlies
o Bevat gehoorbeentjes
Hamer (malleus), aambeeld
(incus) & stijgbeugels
(stapes)
Brengen geluid over v
trommelvlies nr slakkenhuis (cochlea) via membraan v/h
ovale venster (overbrengen lucht vloeistof/water)
Stijgbeugel maakt kleinere maar sterkere bewegingen tegen
slakkenhuid dan trommelvlies o/d hamer
Binnenoor
o Slakkenhuis (cochlea): 2 & ¾ windingen v/e taps toelopende
tunnel
Tunnel (cochleaire kamer) = onderverdeeld in 3
compartimenten
- Scala vestibuli
- Scala media
- Scala tympani
Benen basisstructuur of modiolus
Receptief orgaan: orgaan v Corti / spiraalorgaan
- Ligt op het basiliair membraan (soepelste)
- Tectoriaal membraan (tectum = dak stijver)
- Haarcellen
o Hebben cilia = trilharen
o Bevestigd aan basiliair membraan via steuncellen
o Binnenste haarcellen: cilia raken tectoraal
membraan NIET
o Buitenste haarcellen: wél
, Vocht
o Perilymfe
Scala vestibuli & tympani
Samenstelling ~ CSV (NA+ > K+)
o Endolymfe
Scala media
Samenstelling ~ intracellulair vocht (K+ > NA+) positiever
dan perilymfe
3. Haarcellen & transductie
Basismechanisme: vibratie-energie uitgeoefend o/h
membraan v/h ovaal venster
buigingen i/h basiliair membraan, frequentie-afh
(tonotopisch)
o Hoge tonen: grootste buiging vlakbij basis
o Lage tonen: grootste buiging vlakbij apex
o Basiliair membraan:
Veel breder aan de apex dan aan basis
Veel soepeler aan apex dan aan basis
drukveranderingen in vloeistof opgevangen door
rond venster (bufferen, compenseren)
Buitenste haarcellen (ca 12.000/oor)
o NT voldoende voor horen!
o Mechanische invloed op baliliair membraan
o Top v/d cilia verbonden aan tectoriaal membraan
cruciaal vr fine tuning: kunnen veranderen v lengte onder
efferente invloed (noodzakelijk vr nauwkeuriger onderscheid v
frequenties)
Binnenste haarcellen (ca 3500/oor)
o Essentieel voor horen
o Top v/d cilia NIET verbonden aan tectoriaal membraan
o Ongelijke buigingen in tectoriaal & basiliair membraan tgv
geluidsgolven
o Stromingen i/d vloeistof veroorzaken buigingen i/d cilia
o Opbouw uit proteïne actine met daarrond myosine maakt haarcellen
stijf
o Tip links verbinden top v 1 haarcel met zijkant v/e andere thv
insertional plaques
bewegen v binnenste haarcellen = transductie
Transductie
o Tip links staan onder enige spanning (als een veer)
o Vloeistofstroom richting grootste/kleinste cilium zal spanning ↑ /
↓
o Aanhechtingspunten bevatten elk 1 kation-kanaal (TRPA1)
, o Tip-links openen/sluiten kanalen als sluisdeuren
o Veroorzaakt toename/afname influx v K+ionen depolarisatie
(toename afscheiding glutamaat)
4. Het auditieve circuit
* gehoorzenuw
° bundel v axonen v bipolaire neuronen
° cellichamen in spiraalganglion (ganglioncellen)
° verbindt haarcellen met medulla
*efferente (hersenen cochlea) & afferente connecties (omgekeerd)
* belangrijkste efferent:
Nucleus olivaris olivocochleaire bundel cochlea
Inhiberende invloed op haarcellen (Ach)
Bescherming tegen luid geluid & selectief luisteren
* subcorticale structuren
Complexe subcorticale circuits
Nucleus olivaris superior
o Veel neuronen input v beide oren
o Kleine ≠ in luiheid & timing uitvergroot
lokalisatie (betrokkenheid
trapezelichaampjes)
Laterale leminiscus
o Hoofdzakelijk informatie v contralateraal
oor
o Betrokken bij auditieve reflexen
(vb: verbindingen met de reticulaire formatie =
betrokken bij de autidieve schrikreflex die je wekker
teweeg kan brengen)
Inferieure colliculus
o ≠ typische responsen, tonotopische
patronen, cellen die spontaan vuren behalve bij geluid (~OFF-cellen
visueel systeem), sommige cellen selectief
gevoelig aan bewegende geluidsbronnen,…
(gedeeltelijk) tonotopische organisatie in cochleaire
nuclei, inferieure colliculus, mediale knievormige kern
geur
GEHOOR
1. De stimulus: geluid
* trillende objecten doen luchtmoleculen bewegen
* veroorzaken luchtdrukverschillen = luchtdrukgolven (afwisseling
compressie/ijle lucht)
* waarneembaar voor mensen: frequentie tss 30-20.000/sec
(Hz)
* frequentie = toonhoogte
* amplitude = volume
* mengeling/boventonen = timbre
2. Anatomie v/h oor
Opdeling:
Buitenoor = pinna
o Gehoorkanaal tot trommelvlies
o Vorm v oor draagt bij aan
lokalisatie v geluid MAAR
flexibel vermogen
Middenoor
o Holle ruimte achter trommelvlies
o Bevat gehoorbeentjes
Hamer (malleus), aambeeld
(incus) & stijgbeugels
(stapes)
Brengen geluid over v
trommelvlies nr slakkenhuis (cochlea) via membraan v/h
ovale venster (overbrengen lucht vloeistof/water)
Stijgbeugel maakt kleinere maar sterkere bewegingen tegen
slakkenhuid dan trommelvlies o/d hamer
Binnenoor
o Slakkenhuis (cochlea): 2 & ¾ windingen v/e taps toelopende
tunnel
Tunnel (cochleaire kamer) = onderverdeeld in 3
compartimenten
- Scala vestibuli
- Scala media
- Scala tympani
Benen basisstructuur of modiolus
Receptief orgaan: orgaan v Corti / spiraalorgaan
- Ligt op het basiliair membraan (soepelste)
- Tectoriaal membraan (tectum = dak stijver)
- Haarcellen
o Hebben cilia = trilharen
o Bevestigd aan basiliair membraan via steuncellen
o Binnenste haarcellen: cilia raken tectoraal
membraan NIET
o Buitenste haarcellen: wél
, Vocht
o Perilymfe
Scala vestibuli & tympani
Samenstelling ~ CSV (NA+ > K+)
o Endolymfe
Scala media
Samenstelling ~ intracellulair vocht (K+ > NA+) positiever
dan perilymfe
3. Haarcellen & transductie
Basismechanisme: vibratie-energie uitgeoefend o/h
membraan v/h ovaal venster
buigingen i/h basiliair membraan, frequentie-afh
(tonotopisch)
o Hoge tonen: grootste buiging vlakbij basis
o Lage tonen: grootste buiging vlakbij apex
o Basiliair membraan:
Veel breder aan de apex dan aan basis
Veel soepeler aan apex dan aan basis
drukveranderingen in vloeistof opgevangen door
rond venster (bufferen, compenseren)
Buitenste haarcellen (ca 12.000/oor)
o NT voldoende voor horen!
o Mechanische invloed op baliliair membraan
o Top v/d cilia verbonden aan tectoriaal membraan
cruciaal vr fine tuning: kunnen veranderen v lengte onder
efferente invloed (noodzakelijk vr nauwkeuriger onderscheid v
frequenties)
Binnenste haarcellen (ca 3500/oor)
o Essentieel voor horen
o Top v/d cilia NIET verbonden aan tectoriaal membraan
o Ongelijke buigingen in tectoriaal & basiliair membraan tgv
geluidsgolven
o Stromingen i/d vloeistof veroorzaken buigingen i/d cilia
o Opbouw uit proteïne actine met daarrond myosine maakt haarcellen
stijf
o Tip links verbinden top v 1 haarcel met zijkant v/e andere thv
insertional plaques
bewegen v binnenste haarcellen = transductie
Transductie
o Tip links staan onder enige spanning (als een veer)
o Vloeistofstroom richting grootste/kleinste cilium zal spanning ↑ /
↓
o Aanhechtingspunten bevatten elk 1 kation-kanaal (TRPA1)
, o Tip-links openen/sluiten kanalen als sluisdeuren
o Veroorzaakt toename/afname influx v K+ionen depolarisatie
(toename afscheiding glutamaat)
4. Het auditieve circuit
* gehoorzenuw
° bundel v axonen v bipolaire neuronen
° cellichamen in spiraalganglion (ganglioncellen)
° verbindt haarcellen met medulla
*efferente (hersenen cochlea) & afferente connecties (omgekeerd)
* belangrijkste efferent:
Nucleus olivaris olivocochleaire bundel cochlea
Inhiberende invloed op haarcellen (Ach)
Bescherming tegen luid geluid & selectief luisteren
* subcorticale structuren
Complexe subcorticale circuits
Nucleus olivaris superior
o Veel neuronen input v beide oren
o Kleine ≠ in luiheid & timing uitvergroot
lokalisatie (betrokkenheid
trapezelichaampjes)
Laterale leminiscus
o Hoofdzakelijk informatie v contralateraal
oor
o Betrokken bij auditieve reflexen
(vb: verbindingen met de reticulaire formatie =
betrokken bij de autidieve schrikreflex die je wekker
teweeg kan brengen)
Inferieure colliculus
o ≠ typische responsen, tonotopische
patronen, cellen die spontaan vuren behalve bij geluid (~OFF-cellen
visueel systeem), sommige cellen selectief
gevoelig aan bewegende geluidsbronnen,…
(gedeeltelijk) tonotopische organisatie in cochleaire
nuclei, inferieure colliculus, mediale knievormige kern