Page 1 of 12
Digestion
Purpose:
Heterotrophs – Organisms that eat other plants or animals for energy and nutrients
Animals obtain their food from plants and usually comes in a complex insoluble form. In order for animals
to really get the benefits of the food, they first need to break it down into smaller, more soluble nutrients.
Animals need food as it:
Provides energy for the animal.
The highest concentration of energy is found in fats and carbohydrates.
Provides the proteins necessary for growth and repair of damaged tissues.
Provides vitamins and minerals to regulate body processes (homeostasis), and keep our bodies
fit and healthy.
Ingestion Digestion Asorption Assimilation Egestion
Food taken into Breakdown of When nutrients When nutrients Process in which
body. insoluble are taken into the are taken from undigested food
macromolecules bloodstream. the bloodstream remains are
into smaller into the cells and removed from
water-soluble are used to build the body as
food molecules. new cell faeces.
Chemical or structures and
mechanical components.
, Page 2 of 12
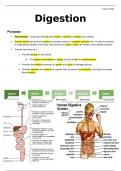
Alimentary Canal
Tube within the body in which food passes and is digested:
Extends from mouth to anus.
Organs:
֍ Mouth, Pharynx, Oesophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine
Associated organs:
֍ Tongue, Salivary Glands, Pancreas, Liver, Gall Bladder
Mouth, Teeth, Tongue and Salivary Glands
Teeth
Humans have 32.
Consists of dentine
Heterodont – An animal which possesses more than a single tooth morphology (shape & size).
Homodont – An animal which possesses teeth that are all of equivalent form (dolphin).
Diphyodont – An animal with two successive sets of teeth (deciduous & permanent set).
Monophyodont – An animal with only one set of teeth during their lifetime.
2: 1: 2: 3
2: 1: 2: 3
Half top & bottom jaw
4×2 2×2 4×2 6×2 Incisors → Canines → Premolars → Molars
Tongue
Muscular organ
Pushes food between teeth.
Mixes food with saliva.
Forms food bolus.
Helps with swallowing by pushing food down throat.
Contains taste buds to taste five different tastes.
The teeth & tongue together are responsible for the mechanical breakdown of food; large pieces are
broken into smaller manageable pieces, and then mixed with saliva to start chemical digestion.
Three Paired Salivary Glands
The salivary glands are exocrine glands.
Parotid glands (under ears)
Sub-mandibular glands (below jaw)
Sublingual glands (under tongue)
Digestion
Purpose:
Heterotrophs – Organisms that eat other plants or animals for energy and nutrients
Animals obtain their food from plants and usually comes in a complex insoluble form. In order for animals
to really get the benefits of the food, they first need to break it down into smaller, more soluble nutrients.
Animals need food as it:
Provides energy for the animal.
The highest concentration of energy is found in fats and carbohydrates.
Provides the proteins necessary for growth and repair of damaged tissues.
Provides vitamins and minerals to regulate body processes (homeostasis), and keep our bodies
fit and healthy.
Ingestion Digestion Asorption Assimilation Egestion
Food taken into Breakdown of When nutrients When nutrients Process in which
body. insoluble are taken into the are taken from undigested food
macromolecules bloodstream. the bloodstream remains are
into smaller into the cells and removed from
water-soluble are used to build the body as
food molecules. new cell faeces.
Chemical or structures and
mechanical components.
, Page 2 of 12
Alimentary Canal
Tube within the body in which food passes and is digested:
Extends from mouth to anus.
Organs:
֍ Mouth, Pharynx, Oesophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine
Associated organs:
֍ Tongue, Salivary Glands, Pancreas, Liver, Gall Bladder
Mouth, Teeth, Tongue and Salivary Glands
Teeth
Humans have 32.
Consists of dentine
Heterodont – An animal which possesses more than a single tooth morphology (shape & size).
Homodont – An animal which possesses teeth that are all of equivalent form (dolphin).
Diphyodont – An animal with two successive sets of teeth (deciduous & permanent set).
Monophyodont – An animal with only one set of teeth during their lifetime.
2: 1: 2: 3
2: 1: 2: 3
Half top & bottom jaw
4×2 2×2 4×2 6×2 Incisors → Canines → Premolars → Molars
Tongue
Muscular organ
Pushes food between teeth.
Mixes food with saliva.
Forms food bolus.
Helps with swallowing by pushing food down throat.
Contains taste buds to taste five different tastes.
The teeth & tongue together are responsible for the mechanical breakdown of food; large pieces are
broken into smaller manageable pieces, and then mixed with saliva to start chemical digestion.
Three Paired Salivary Glands
The salivary glands are exocrine glands.
Parotid glands (under ears)
Sub-mandibular glands (below jaw)
Sublingual glands (under tongue)