Week 6 :
Preparation: Chap 10: Monopoly, Market
power
Monopoly: market that has only one seller but many buyers.
Monopsony: market that has only one buyer and many sellers.
Market power: Ability of a seller or buyer to affect the price of a good.
Monopoly
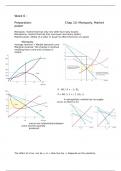
Average revenue = Market demand curve
Marginal revenue: The change in revenue
resulting from a one-unit increase in
output.
P – MC / P = - 1 / Eld
P = MC / ( 1 + ( 1 / Eld ) )
A monopolistic market has no supply
curve, so there is no
one-to-one relationship between
price and the quantity
produced.
The effect of a tax: can be > or < than the tax -> Depends on the elasticity.
, Even if a firm is not a monopolist, it can have a monopoly power: can
profitably charge a price greater than marginal cost.
Competitive firm: price equals marginal cost ≠ Firm with monopoly power: price >
marginal cost.
Lerner Index of Monopoly Power: Measure of monopoly power calculated as excess of
price over marginal cost as a fraction of price.
L = (P – MC) / P If a perfect competitive firm: P = MC, so that L = 0. The larger is
L the greater is the degree of monopoly power.
L = (P – MC) / P = - 1 / Eld.
The less elastic its demand curve, the more monopoly power a firm has. 3 factors to
determine a firm elasticity:
- The elasticity of market demand: limit the potential for monopoly power.
- The number of firms in the market: the more the less impacting. Small
number: highly concentrated. Competitive strategy= barrier entry: Condition
that impedes entry by new competitors.
- The Number of Firms: Each one will try to get as much as the market as it can.
Collusion can generate substantial monopoly power.
Preparation: Chap 10: Monopoly, Market
power
Monopoly: market that has only one seller but many buyers.
Monopsony: market that has only one buyer and many sellers.
Market power: Ability of a seller or buyer to affect the price of a good.
Monopoly
Average revenue = Market demand curve
Marginal revenue: The change in revenue
resulting from a one-unit increase in
output.
P – MC / P = - 1 / Eld
P = MC / ( 1 + ( 1 / Eld ) )
A monopolistic market has no supply
curve, so there is no
one-to-one relationship between
price and the quantity
produced.
The effect of a tax: can be > or < than the tax -> Depends on the elasticity.
, Even if a firm is not a monopolist, it can have a monopoly power: can
profitably charge a price greater than marginal cost.
Competitive firm: price equals marginal cost ≠ Firm with monopoly power: price >
marginal cost.
Lerner Index of Monopoly Power: Measure of monopoly power calculated as excess of
price over marginal cost as a fraction of price.
L = (P – MC) / P If a perfect competitive firm: P = MC, so that L = 0. The larger is
L the greater is the degree of monopoly power.
L = (P – MC) / P = - 1 / Eld.
The less elastic its demand curve, the more monopoly power a firm has. 3 factors to
determine a firm elasticity:
- The elasticity of market demand: limit the potential for monopoly power.
- The number of firms in the market: the more the less impacting. Small
number: highly concentrated. Competitive strategy= barrier entry: Condition
that impedes entry by new competitors.
- The Number of Firms: Each one will try to get as much as the market as it can.
Collusion can generate substantial monopoly power.