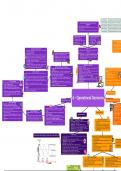
OBJECTIVES AND THEIR EFFECT ON THE METHOD OF
PRODUCTION:
Improving quality might use job or cell
Improving efficiency, dependability and speed of response might
use batch or flow
Environmental, efficiency and quality met with lean production
INTERNAL FACTORS INFLUENCING EXTERNAL FACTORS INFLUENCING
Nature of a product Competitor’s performance
Availability of resources Market conditions
Decisions and objectives of the other Demand for product CONSIDERING HOW CAPA
departments Changing customer needs CHANGE OVE
The overall objective New technology The key to long-term suc
changes to match demand
but not totally accurate an
RELATIONSHIPS WITH SUPPLIERS ADDED VALUE Short-term changes prov
Strategic working relationship - both companies can get the long term Added Value = sales revenue - cost of bought in goods and Long-term predictions if
benefits of working together services lower unit costs
Can build these relationships by: HOW THE SUPPLY CHAIN ADAPTS TO DEMAND Adding value is an important objective and will usually
Linked Networks - shared IT systems e.g. inventory stock control retailer - hire more peripheral workers increase profits, can be achieved by increasing selling price or
management, electronic data interchange allow for both supplier and distributor - increase deliveries by outsourcing reducing costs of raw materials, customers will pay more for
company to view stock levels - improves efficiency and cuts cost manufacturer - temp increase capacity utilisation, more value but value isn’t just money it can be a benefit from
JIT Systems - having the right amount of materials at the right time, get more materials from alt supplier any of the below targets
less waste and less need for storage space suppliers - supply more raw material
Shared Costs - businesses and suppliers can share storage and use of
specialised equipment
Innovation - if companies work closely together they can share ideas OPERATIONAL OBJECTIVES
and save money through innovation e.g. improve manufacturing =Targets set for production
process, developing products, altering supply network IMPROVING OPERATIONAL PERFORMANCE
working closely with the right suppliers will improve operational QUALITY - maintaining or improving or reducing complaints Capacity is maximum output a company can produce
performance COSTS - cut costs, restructure given period of time without buying more fixed asse
CHOOSING SUPPLIERS productivity will increase - costs will fall and profits will increase FLEXIBILITY - react to what people want, varied volume based on Depends on…
Most effective suppliers are the ones who meet your business' needs so must efficient supply chains can meet customer expectations easier demand, seasonality, zero hour contracts? No. of employees
consider ... Should always be looking for ways to improve: EFFICIENCY - making better use of resources, capacity utilisation, Technology and the state of it
Price - the total cost of acquiring a product, the cheaper the supplier the only buy the supplies you really need improving labour and capital productivity The production process
more value added but the cheapest supplier isn't always the best understanding the difference between a strategic supplier and a non INNOVATION - R&D Investment in the business
Payment Terms - how much needs to be paid, how and by when. New strategic supplier - spend more time selecting and managing the ENVIRONMENT - cutting carbon emissions, recycle more
companies often have to pay up front, established companies can be given strategic supplier SPEED OF RESPONSE - decreasing production time or waiting time Capacity Utilization is how much a business is using
SUPPLY AND DEMAND credit limit the number of sources you buy from - easier and more cost DEPENDABILITY
MASS CUSTOMISATION - supply tailor made products Quality - needs to be consistent, customers are selective effective, but don't have just one supplier cuz if they have a problem Capacity Utilisation (%) = Output / Capacity X 100
a method of producing to order Capacity - need suppliers who can meet peaks in demand, buying in bulk can you have no other options
products are made after the order is placed get discounts always have an alt supply source ready if needed
combines flexibility with low costs of mass production Reliability
must have a flexible and efficient production process and supply Flexibility - need to be able to respond to businesses requirements e.g. short
chain notice changes or environmental goals
cheap increase in customer choice, competitive advantage
is difficult to make efficient and profitable - customised CAPACITY UTILISATION
products can be expensive and take a long time which is only
4 - Operational Decisions
okay for luxury items
MANAGING SUPPLY CHAINS INCREASING EFFICIENCY AND PRODUCTIVITY
SUPPLY AND DEMAND
OUTSOURCING - help meet changes in demand PRODUCTIVITY
contracting some activities to other businesses Productivity = the meas
can outsource some or all of the product manufacturing SUPPLY CHAINS given time period
might also outsource things they need but don't specialise in e.g. supply chain = the group of firms that are involved in all the Efficiency = about getti
finance, recruitment, advertising, IT various processes required to make the finished product or amount of inputs - redu
benefits business cuz they can accept contracts they would have SUPPLY AND DEMAND service decrease unit cost and i
otherwise turned down PERIPHERAL WORKERS - help meet changes in begins with provider of raw material and ends with who sells IMPROVING QUALITY
can benefit from specialised knowledge of outsource business demand the finished product Labour productivity - m
MANAGING INVENTORY employee produces
reduced costs - don't have to permanently pay for outsourced employees who aren't essential but are employed members will vary based on type of product or service
staff by the business when they need more staff tend to be; suppliers, manufacturers, distributors and retailers Labour productivity = out
disadvantage - no control over quality the outsource business keep fixed costs down by employing them on everyone needs to be reliable and dependable empl
produces zero-hour, temp or part-time contracts businesses need to be flexible on time taken and volume - HOLDING STOCK = COSTLY WHY QUALITY IS IMPORTANT
sudden changes in demand can be met by outsourcing or utilising Stock includes: raw materials, materials for products in poor quality leads to customer dissatisfaction and As labour productivity i
a flexible workforce process and finished products a bad rep unit falls
suppliers with faster response have a competitive advantage Storage costs - rent, heating, lighting, security most customers know that lower price = lower
Wastage costs - cost of throwing away useless stock, stock quality but still expect it to be fit for purpose
goes out of date or fashion or gets damaged in holding high quality products allows for premium pricing
Opportunity cost - the cost of investing in stock instead of - can also give workers pride in their work and
something else = IT IS UNPRODUCTIVE increase morale
Reorder level = lead time (days) X avg daily usage + buffer stock level STOCK CONTROL
max stock level of a business depends on size of warehouse, methods of production HOW HIGH QUALITY CAN REDUCE COSTS AND INCREASE REVENUE
and opportunity costs less raw materials, less worker and less machinery's time gets
flow production = requires a large stock of raw materials used up by mistakes LIMITATIONS TO
batch production = requires a large stock of work in progress products high quality products don't need as much promotion for retailers Can be difficult t
job production = NO stock of finished goods and customers limit to how muc
cell production = JIT stock control fewer complaints and refunds - more time for employees to focus workers have to
Buffer stock = minimum level of stock - needed so don't run out on quality dwelling costs ti
Amount of buffer stock depends on storage, the type of product (is it perishable?), don't need discount prices to sell damaged stock if outsource work
the rate in which stocks are used up and the lead time high quality can be a USP
lead time = the time it takes for the goods to arrive after placing the order improves rep and image
the longer the lead time, the more buffer stock needed makes it easy to keep customers and attract new ones
reorder quantity = amount the company orders from supplier
reorder level = the stock level that triggers a reorder
QUALITY CONTROL QUALITY ASSURANCE
= checking goods as you make them or when they arrive from = introducing measures into the production process t
suppliers - often done by specially trained quality inspectors things can't go wrong in the first place
assumes that errors are unavoidable aims to prevent errors instead of eliminating faulty g
detects errors and puts them right assumes errors are avoidable
inspectors check other people's work and are then responsible for employees check their own work - workers are resp
ADVANTAGES OF TQM the quality passing on good quality to the next stage
help bond as a team
boosts a company's rep
PRODUCTION:
Improving quality might use job or cell
Improving efficiency, dependability and speed of response might
use batch or flow
Environmental, efficiency and quality met with lean production
INTERNAL FACTORS INFLUENCING EXTERNAL FACTORS INFLUENCING
Nature of a product Competitor’s performance
Availability of resources Market conditions
Decisions and objectives of the other Demand for product CONSIDERING HOW CAPA
departments Changing customer needs CHANGE OVE
The overall objective New technology The key to long-term suc
changes to match demand
but not totally accurate an
RELATIONSHIPS WITH SUPPLIERS ADDED VALUE Short-term changes prov
Strategic working relationship - both companies can get the long term Added Value = sales revenue - cost of bought in goods and Long-term predictions if
benefits of working together services lower unit costs
Can build these relationships by: HOW THE SUPPLY CHAIN ADAPTS TO DEMAND Adding value is an important objective and will usually
Linked Networks - shared IT systems e.g. inventory stock control retailer - hire more peripheral workers increase profits, can be achieved by increasing selling price or
management, electronic data interchange allow for both supplier and distributor - increase deliveries by outsourcing reducing costs of raw materials, customers will pay more for
company to view stock levels - improves efficiency and cuts cost manufacturer - temp increase capacity utilisation, more value but value isn’t just money it can be a benefit from
JIT Systems - having the right amount of materials at the right time, get more materials from alt supplier any of the below targets
less waste and less need for storage space suppliers - supply more raw material
Shared Costs - businesses and suppliers can share storage and use of
specialised equipment
Innovation - if companies work closely together they can share ideas OPERATIONAL OBJECTIVES
and save money through innovation e.g. improve manufacturing =Targets set for production
process, developing products, altering supply network IMPROVING OPERATIONAL PERFORMANCE
working closely with the right suppliers will improve operational QUALITY - maintaining or improving or reducing complaints Capacity is maximum output a company can produce
performance COSTS - cut costs, restructure given period of time without buying more fixed asse
CHOOSING SUPPLIERS productivity will increase - costs will fall and profits will increase FLEXIBILITY - react to what people want, varied volume based on Depends on…
Most effective suppliers are the ones who meet your business' needs so must efficient supply chains can meet customer expectations easier demand, seasonality, zero hour contracts? No. of employees
consider ... Should always be looking for ways to improve: EFFICIENCY - making better use of resources, capacity utilisation, Technology and the state of it
Price - the total cost of acquiring a product, the cheaper the supplier the only buy the supplies you really need improving labour and capital productivity The production process
more value added but the cheapest supplier isn't always the best understanding the difference between a strategic supplier and a non INNOVATION - R&D Investment in the business
Payment Terms - how much needs to be paid, how and by when. New strategic supplier - spend more time selecting and managing the ENVIRONMENT - cutting carbon emissions, recycle more
companies often have to pay up front, established companies can be given strategic supplier SPEED OF RESPONSE - decreasing production time or waiting time Capacity Utilization is how much a business is using
SUPPLY AND DEMAND credit limit the number of sources you buy from - easier and more cost DEPENDABILITY
MASS CUSTOMISATION - supply tailor made products Quality - needs to be consistent, customers are selective effective, but don't have just one supplier cuz if they have a problem Capacity Utilisation (%) = Output / Capacity X 100
a method of producing to order Capacity - need suppliers who can meet peaks in demand, buying in bulk can you have no other options
products are made after the order is placed get discounts always have an alt supply source ready if needed
combines flexibility with low costs of mass production Reliability
must have a flexible and efficient production process and supply Flexibility - need to be able to respond to businesses requirements e.g. short
chain notice changes or environmental goals
cheap increase in customer choice, competitive advantage
is difficult to make efficient and profitable - customised CAPACITY UTILISATION
products can be expensive and take a long time which is only
4 - Operational Decisions
okay for luxury items
MANAGING SUPPLY CHAINS INCREASING EFFICIENCY AND PRODUCTIVITY
SUPPLY AND DEMAND
OUTSOURCING - help meet changes in demand PRODUCTIVITY
contracting some activities to other businesses Productivity = the meas
can outsource some or all of the product manufacturing SUPPLY CHAINS given time period
might also outsource things they need but don't specialise in e.g. supply chain = the group of firms that are involved in all the Efficiency = about getti
finance, recruitment, advertising, IT various processes required to make the finished product or amount of inputs - redu
benefits business cuz they can accept contracts they would have SUPPLY AND DEMAND service decrease unit cost and i
otherwise turned down PERIPHERAL WORKERS - help meet changes in begins with provider of raw material and ends with who sells IMPROVING QUALITY
can benefit from specialised knowledge of outsource business demand the finished product Labour productivity - m
MANAGING INVENTORY employee produces
reduced costs - don't have to permanently pay for outsourced employees who aren't essential but are employed members will vary based on type of product or service
staff by the business when they need more staff tend to be; suppliers, manufacturers, distributors and retailers Labour productivity = out
disadvantage - no control over quality the outsource business keep fixed costs down by employing them on everyone needs to be reliable and dependable empl
produces zero-hour, temp or part-time contracts businesses need to be flexible on time taken and volume - HOLDING STOCK = COSTLY WHY QUALITY IS IMPORTANT
sudden changes in demand can be met by outsourcing or utilising Stock includes: raw materials, materials for products in poor quality leads to customer dissatisfaction and As labour productivity i
a flexible workforce process and finished products a bad rep unit falls
suppliers with faster response have a competitive advantage Storage costs - rent, heating, lighting, security most customers know that lower price = lower
Wastage costs - cost of throwing away useless stock, stock quality but still expect it to be fit for purpose
goes out of date or fashion or gets damaged in holding high quality products allows for premium pricing
Opportunity cost - the cost of investing in stock instead of - can also give workers pride in their work and
something else = IT IS UNPRODUCTIVE increase morale
Reorder level = lead time (days) X avg daily usage + buffer stock level STOCK CONTROL
max stock level of a business depends on size of warehouse, methods of production HOW HIGH QUALITY CAN REDUCE COSTS AND INCREASE REVENUE
and opportunity costs less raw materials, less worker and less machinery's time gets
flow production = requires a large stock of raw materials used up by mistakes LIMITATIONS TO
batch production = requires a large stock of work in progress products high quality products don't need as much promotion for retailers Can be difficult t
job production = NO stock of finished goods and customers limit to how muc
cell production = JIT stock control fewer complaints and refunds - more time for employees to focus workers have to
Buffer stock = minimum level of stock - needed so don't run out on quality dwelling costs ti
Amount of buffer stock depends on storage, the type of product (is it perishable?), don't need discount prices to sell damaged stock if outsource work
the rate in which stocks are used up and the lead time high quality can be a USP
lead time = the time it takes for the goods to arrive after placing the order improves rep and image
the longer the lead time, the more buffer stock needed makes it easy to keep customers and attract new ones
reorder quantity = amount the company orders from supplier
reorder level = the stock level that triggers a reorder
QUALITY CONTROL QUALITY ASSURANCE
= checking goods as you make them or when they arrive from = introducing measures into the production process t
suppliers - often done by specially trained quality inspectors things can't go wrong in the first place
assumes that errors are unavoidable aims to prevent errors instead of eliminating faulty g
detects errors and puts them right assumes errors are avoidable
inspectors check other people's work and are then responsible for employees check their own work - workers are resp
ADVANTAGES OF TQM the quality passing on good quality to the next stage
help bond as a team
boosts a company's rep