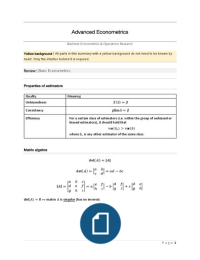
#1. During the inspection process, restorers shall make a reasonable effort to - ANSWER-C. identify and address potential safety hazards
#2. A significant amount of water absorption and evaporation load where wet porous materials represent ~5% to ~40% of combined ceiling, walls, and flooring surface areas and where low evaporation materials and assemblies are minimally wet is - ANSWER-
B. class 2
#3. Multiple extraction of salvageable materials, especially porous material (e.g. Carpet , cushion) often are required to: - ANSWER-decrease drying time
#4. To enhance drying, restorers should manage both ambient temperature and - ANSWER-surface temperatures of affected materials
#5. Water damage restoration services should not begin until after the: - ANSWER-
restorer has entered into an adequately written contract.
#6. Two tools that should be used to properly disengage most stretched-in carpet - ANSWER-Knee kicker and carpet awl
#7. When inspecting a water damage structure, restorers should inspect: - ANSWER-all
potentially affected areas.
#8. Buckled or damaged particle board should - ANSWER-removed and replaced with new material.
#9. upon entering a building, professional moisture detection equipment should be used
to evaluate and document: - ANSWER-applicable psychrometric conditions and moisture content or level readings .
#10. When wet, a structural material that loses most of its structural integrity, but regains its strength when dry, is: - ANSWER-Concrete
#11 Initially, a method of search for abnormal moisture behind ceramic tile or resilient flooring can be accomplished by - ANSWER-using a non-penetrating (non-invasive) moisture meter
#12. To minimize damage and reduce drying time, reduce drying time, restorers should:
- ANSWER-begin mitigation as soon as safely possible
#13. The moisture content of structural materials should be measured with a - ANSWER-A. moisture meter #14. When accessible from below, to dry wet wood subflooring under stone or tile flooring, restorers can use low-humidity air and - ANSWER-D. vapor barrier
#15. Biocides designed to destroy or eliminate all forms of microbial life and their spores
are - ANSWER-D. sterilizers
#16. When carpet is wet it can be delaminated by - ANSWER-D. improper handling and disengaging
#17. To minimize or control aerosolized soils or contaminants during restoration, restorers can: - ANSWER-B. install one or more air filtration devices (AFDs)
#18. When pre-existing damage is discovered, restorer should - ANSWER-D. document
and bring it to the attention of materially interested parties
#19. Rapid drying of structural materials is achieved by - ANSWER-A. promoting evaporation and dehumidification or ventilation
#20. When carpet and cushion (pad, underlay) are saturated with Category 3 water - ANSWER-B. Both should be removed for proper disposal
#21. To minimize safety concerns and to speed structural drying, gypsum board (drywall) ceilings that are saturated and sagging should be - ANSWER-A. drained, removed quickly, and properly disposed
#22. The force exerted by water molecules in the air on surrounding surfaces is - ANSWER-b. Vapor Pressure (page 11)
#23. Generally, fastest rate of evaporation from wet materials with a 70F (21C) surface temperature [0.67 VP] would be an environment with - ANSWER-A. 60F (4C) and 80% RH
#24. Two hazardous materials more likely found in older building that require compliance with laws and regulations when handled are - ANSWER-C. lead-based paint and asbestos
#25. As humidity ratio increases (or decreases) another psychrometric chart property that also increases (or decreases) is - ANSWER-C. vapor pressure
#26. Ventilating a structure during the initial stages of restoration can be effective way to
enhance drying by reducing the build up of - ANSWER-C. humidity
#27. When using government-registered biocide, restorers shall - ANSWER-C. apply according to label directions