Question 1
The first and second laws of thermodynamics have significant implications for the processes of
production and consumption in the economy.
The first law of thermodynamics, also known as the law of conservation of energy, states that energy
can neither be created nor destroyed but can only change forms. This law has implications for the
production processes in the economy because it highlights the importance of energy efficiency. It
implies that the total amount of energy input into a production process must equal the total amount
of energy output, taking into account any energy losses due to inefficiencies or waste. This means
that in the production of goods and services, it is crucial to minimize energy waste and optimize
energy use to ensure that the economy operates within the constraints of this law.
The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system tends to increase
over time, leading to the degradation of energy and the production of waste heat. This law has
implications for both production and consumption in the economy. From a production standpoint, it
implies that there are limits to the efficiency of energy conversion processes, and that some energy
will always be lost in the form of waste heat. This highlights the importance of improving the
efficiency of production processes to minimize waste and increase overall productivity.
From a consumption standpoint, the second law of thermodynamics implies that the resources used
to generate goods and services are finite and that there are limits to the capacity of the environment
to absorb waste generated from consumption. This suggests that sustainable consumption practices
are essential for the long-term health of the economy and the environment.
In summary, the first and second laws of thermodynamics have significant implications for the
processes of production and consumption in the economy. They highlight the importance of energy
efficiency, the limits to energy conversion processes, and the need for sustainable consumption
practices to ensure the long-term sustainability of the economy and the environment.
, Question 2
The aquamarine principle states that a rational decision-maker will allocate resources in such a way
that the marginal benefit of the last unit of each resource is the same for all resources. In the case of
a factory with two plants, one with steeply increasing marginal costs and one with more slowly
increasing marginal costs, the factory should produce at the point where the marginal cost of
producing one more unit of a good is equal between both plants.
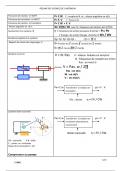
In the graph below, the x-axis represents the quantity of output produced by the factory, and the y-
axis represents the marginal cost of producing that output. The red line represents the marginal cost
of the plant with steeply increasing marginal costs, while the blue line represents the marginal cost
of the plant with more slowly increasing marginal cost.
Graphically, the equimarginal principle can be shown as follows:
The equimarginal principle as illustrated by the graph can be used to minimize the cost of production
a great deal by reducing the cost of producing a given quantity output. The minimization of the
production cost is mainly achieved through the distribution of the cost of production of the firm in
order to realize the same marginal costs across the production sources according to the graph.
The first and second laws of thermodynamics have significant implications for the processes of
production and consumption in the economy.
The first law of thermodynamics, also known as the law of conservation of energy, states that energy
can neither be created nor destroyed but can only change forms. This law has implications for the
production processes in the economy because it highlights the importance of energy efficiency. It
implies that the total amount of energy input into a production process must equal the total amount
of energy output, taking into account any energy losses due to inefficiencies or waste. This means
that in the production of goods and services, it is crucial to minimize energy waste and optimize
energy use to ensure that the economy operates within the constraints of this law.
The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system tends to increase
over time, leading to the degradation of energy and the production of waste heat. This law has
implications for both production and consumption in the economy. From a production standpoint, it
implies that there are limits to the efficiency of energy conversion processes, and that some energy
will always be lost in the form of waste heat. This highlights the importance of improving the
efficiency of production processes to minimize waste and increase overall productivity.
From a consumption standpoint, the second law of thermodynamics implies that the resources used
to generate goods and services are finite and that there are limits to the capacity of the environment
to absorb waste generated from consumption. This suggests that sustainable consumption practices
are essential for the long-term health of the economy and the environment.
In summary, the first and second laws of thermodynamics have significant implications for the
processes of production and consumption in the economy. They highlight the importance of energy
efficiency, the limits to energy conversion processes, and the need for sustainable consumption
practices to ensure the long-term sustainability of the economy and the environment.
, Question 2
The aquamarine principle states that a rational decision-maker will allocate resources in such a way
that the marginal benefit of the last unit of each resource is the same for all resources. In the case of
a factory with two plants, one with steeply increasing marginal costs and one with more slowly
increasing marginal costs, the factory should produce at the point where the marginal cost of
producing one more unit of a good is equal between both plants.
In the graph below, the x-axis represents the quantity of output produced by the factory, and the y-
axis represents the marginal cost of producing that output. The red line represents the marginal cost
of the plant with steeply increasing marginal costs, while the blue line represents the marginal cost
of the plant with more slowly increasing marginal cost.
Graphically, the equimarginal principle can be shown as follows:
The equimarginal principle as illustrated by the graph can be used to minimize the cost of production
a great deal by reducing the cost of producing a given quantity output. The minimization of the
production cost is mainly achieved through the distribution of the cost of production of the firm in
order to realize the same marginal costs across the production sources according to the graph.