Samenvatting
Summary PSY2013 / IPN1023 - Task 3
- Vak
- Instelling
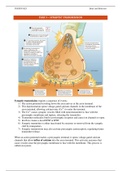
Elaborate and complete summary of the third task of the course Body and Behavior (PSY1023 / IPN1023). Summary contains a lot of figures. Resources used: parts of Carlson (2017), Breedlove (2017) or Pinel (2017). All tasks available as bundle!
[Meer zien]