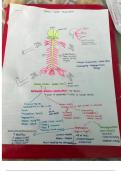
Summary
Summary Pain Relief in Labour
- Course
- Institution
A 1-4 page document written by a final year medical student with distinction grades in the uploaded modules. These notes are concise and of very high quality - using a combination of textbooks, lectures, and current guidelines (NICE and RCOG). These documents are the only resource you should need f...
[Show more]