Lecture 1
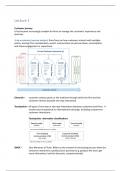
Customer journey
It has become increasingly complex for firms to manage the customers' experience and
journeys.
→ In a customer journey analysis, firms focus on how customers interact with mul>ple
points, moving from considera>on, search, and purchase to post-purchase, consump>on,
and future engagement or repurchase.
Channels = customer contact points or the mediums through which the firm and the
customer interact (exclude one-way interac>on).
Touchpoints = all types of one-way or two-way interac>ons between customers and firms. →
involve any transac>onal or informa>onal exchange. Including customer-to-
customer interac>ons.
Touchpoints- alterna5ve classifica5ons
ZMOT = Zero Moments of Truth. Refers to the moment in the buying process when the
consumer researches a product prior purchase (e.g. going to the store, get
more informa>on, look for discounts, compare brands).
,Different types of customer journeys and implica5ons for brands
Customer journey segments
- Store-focused = customers primarily interac>ng through physical stores.
- Mul>ple touchpoints = customers using mul>ple channels for interac>on.
- Online-to-offline = customers star>ng their journey online and finishing offline.
- Pragma>c online = customers who primarily use online channels in a prac>cal
manner.
- Extensive online = customers heavily relying on online channels for their interac>ons.
Take-aways – Herhausen et al (2019) paper.
- Understand how the increasing importance of mobile devices. It is an addi>onal
search channel that complements other touchpoints rather than replacing them.
- No “showrooming” segment: The threat of showrooming may be overrated.
§ Webrooming: online product research, purchase in store.
§ Showrooming: product research in store, purchase online.
- Importance of physical stores despite increased usage of online & mobile
- Different levers should be used to increase loyalty across different segments.
, Lecture 2
ATribu5on challenges
ATribu5on problem = which marke>ng channel or touchpoints deserves the credit for
influencing a customer’s decision.
1. Single touch = credits to one touchpoint
a. Last interac>on
2. Mul5-touch = credits to mul>ple touchpoints
a. Linear = equal
b. Time decay = credits to touchpoints close to conversion.
Webrooming and showrooming
- Webrooming: online product research, purchase in store.
- Showrooming: product research in store, purchase online.
Mul5-channel strategy =
Businesses uses many ways to reach customers like stores, sites, socials. Focus on managing
and op>mizing the performance of EACH channel.
Omnichannel strategy =
All the ways to reach customers are connected and work together. Focus on integra>ng
ac>vi>es ACROSS channels to correspond to how consumers shop.
Online Distribu5on breadth
Breadth = Refers to how many stores/places/sites carry a brands product. And thus, how
easy it is for consumers to find an online retailer that stocks the brand.
Metrics:
§ Number of visitors
§ Number of online retailers
§ Downloads
Online distribu5on dept
Depth = Looks at how well a brands products are presented and promoted within each
store they are sold. And thus, how easy it is to find the brand within an online
retailer & how a_rac>ve your brand is compared to other retailers online.
Metrics:
§ Product visibility
§ Range of products
§ Quality of shopping experience
Customer journey
It has become increasingly complex for firms to manage the customers' experience and
journeys.
→ In a customer journey analysis, firms focus on how customers interact with mul>ple
points, moving from considera>on, search, and purchase to post-purchase, consump>on,
and future engagement or repurchase.
Channels = customer contact points or the mediums through which the firm and the
customer interact (exclude one-way interac>on).
Touchpoints = all types of one-way or two-way interac>ons between customers and firms. →
involve any transac>onal or informa>onal exchange. Including customer-to-
customer interac>ons.
Touchpoints- alterna5ve classifica5ons
ZMOT = Zero Moments of Truth. Refers to the moment in the buying process when the
consumer researches a product prior purchase (e.g. going to the store, get
more informa>on, look for discounts, compare brands).
,Different types of customer journeys and implica5ons for brands
Customer journey segments
- Store-focused = customers primarily interac>ng through physical stores.
- Mul>ple touchpoints = customers using mul>ple channels for interac>on.
- Online-to-offline = customers star>ng their journey online and finishing offline.
- Pragma>c online = customers who primarily use online channels in a prac>cal
manner.
- Extensive online = customers heavily relying on online channels for their interac>ons.
Take-aways – Herhausen et al (2019) paper.
- Understand how the increasing importance of mobile devices. It is an addi>onal
search channel that complements other touchpoints rather than replacing them.
- No “showrooming” segment: The threat of showrooming may be overrated.
§ Webrooming: online product research, purchase in store.
§ Showrooming: product research in store, purchase online.
- Importance of physical stores despite increased usage of online & mobile
- Different levers should be used to increase loyalty across different segments.
, Lecture 2
ATribu5on challenges
ATribu5on problem = which marke>ng channel or touchpoints deserves the credit for
influencing a customer’s decision.
1. Single touch = credits to one touchpoint
a. Last interac>on
2. Mul5-touch = credits to mul>ple touchpoints
a. Linear = equal
b. Time decay = credits to touchpoints close to conversion.
Webrooming and showrooming
- Webrooming: online product research, purchase in store.
- Showrooming: product research in store, purchase online.
Mul5-channel strategy =
Businesses uses many ways to reach customers like stores, sites, socials. Focus on managing
and op>mizing the performance of EACH channel.
Omnichannel strategy =
All the ways to reach customers are connected and work together. Focus on integra>ng
ac>vi>es ACROSS channels to correspond to how consumers shop.
Online Distribu5on breadth
Breadth = Refers to how many stores/places/sites carry a brands product. And thus, how
easy it is for consumers to find an online retailer that stocks the brand.
Metrics:
§ Number of visitors
§ Number of online retailers
§ Downloads
Online distribu5on dept
Depth = Looks at how well a brands products are presented and promoted within each
store they are sold. And thus, how easy it is to find the brand within an online
retailer & how a_rac>ve your brand is compared to other retailers online.
Metrics:
§ Product visibility
§ Range of products
§ Quality of shopping experience