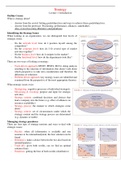
MICROSCOPY Slides
Dry mount = Solid specimen sectioned, cover slip
Microscopes Wet mount = liquid specimen, cover slip at angle
Light microscope Squash slide = wet mount, soft sample, press cover slip
- X200 magnification Smear slide = liquid sample, edge to smear, cover slip
- 200nm resolution
- 400-700nm wavelength Artefacts = structures produced in preparation
- Eyepiece + objective lens (multiplied) - Bubbles (light)
- Cheap, portable, simple prep, no damage, natural - Loss of membrane continuity
colour, living or dead - Organelle distortion
- Empty space in cytoplasm
TEM - Mesosome (inward membrane fold - fixation)
- x500,000-2,000,000 magnification
- 0.5nm resolution Fixing – chemicals to preserve
- Electron beam transmitted through – 3D image Sectioning – dehydrated and into mould
- Thin specimen, denser parts = darker
- Expensive, complex = distortion, black + white, dead Differential staining
- Vacuum = straight electron beam - ↑ contrast as take up stain to different degrees
- Helps identify organelles
SEM - Helps identify different types of cells (distinguish)
- x100,000-500,000 magnification
- 3-10nm resolution + charge = crystal violet + methylene blue (organelles)
- Electron beam across surface - charge = congo red + nigrosine (stain outside cell)
- Reflected electrons collected – 2D image
- Expensive, complex = distortion, black + white, dead Gram stain technique
- Separate bacteria by wall thickness
Laser scanning confocal microscope - Crystal violet, iodine, alcohol wash
- Laser across specimen - g+ bacteria (thick) = blue/purple
- 2D image but 3D if layer focal planes - Safranin dye counterstain
- Non-invasive – eye disease, endoscopic procedures - g- bacteria (thin walls) = red
- Florescence (absorb + reradiate) from dye - g+ bacteria susceptible to penicillin = inhibits cell wall
- Emit ↑ wavelength, filtered through pinhole aperture
- Only use light radiated close to focal plane, light from Acid fast technique
other planes ↓ resolution + blurring - Primary dye = all bacteria red
- Beam splitter (dichroic mirror) reflects laser + - Decolouriser acid = non-acid fast lose red
transmits reflected - Counterstain = non-acid fast turn blue
- Florescent tags for genes to see where travels in cell
Ultrastructure
Nucleus
- Contains DNA
- Controls metabolic activity
- Directs protein synthesis
- Nucleolus contains RNA + proteins = produce ribos
- Double mem nuclear envelope, prevent DNA damage
- Nuclear pores – where RNA molecules leave
I Plasma membrane
M A - Phospholipid bilayer (lipids + proteins)
- Regulate movement of substance (selective perm)
- Receptor molecules
Magnification = times larger the image is than actual
Resolution = ability to distinguish 2 points (detail) Mitochondria
- Limited by diffraction of light, reflections overlap - Matrix = internal enzyme fluid
- Smaller wavelength = higher resolution (electron) - Double membrane, cristae = folded inner membrane
- Mitochondrial DNA + ribosomes = own enzymes
Eyepiece divisions = stage micrometre / graticule divisions - Aerobic respiration – produce energy + ATP
Dry mount = Solid specimen sectioned, cover slip
Microscopes Wet mount = liquid specimen, cover slip at angle
Light microscope Squash slide = wet mount, soft sample, press cover slip
- X200 magnification Smear slide = liquid sample, edge to smear, cover slip
- 200nm resolution
- 400-700nm wavelength Artefacts = structures produced in preparation
- Eyepiece + objective lens (multiplied) - Bubbles (light)
- Cheap, portable, simple prep, no damage, natural - Loss of membrane continuity
colour, living or dead - Organelle distortion
- Empty space in cytoplasm
TEM - Mesosome (inward membrane fold - fixation)
- x500,000-2,000,000 magnification
- 0.5nm resolution Fixing – chemicals to preserve
- Electron beam transmitted through – 3D image Sectioning – dehydrated and into mould
- Thin specimen, denser parts = darker
- Expensive, complex = distortion, black + white, dead Differential staining
- Vacuum = straight electron beam - ↑ contrast as take up stain to different degrees
- Helps identify organelles
SEM - Helps identify different types of cells (distinguish)
- x100,000-500,000 magnification
- 3-10nm resolution + charge = crystal violet + methylene blue (organelles)
- Electron beam across surface - charge = congo red + nigrosine (stain outside cell)
- Reflected electrons collected – 2D image
- Expensive, complex = distortion, black + white, dead Gram stain technique
- Separate bacteria by wall thickness
Laser scanning confocal microscope - Crystal violet, iodine, alcohol wash
- Laser across specimen - g+ bacteria (thick) = blue/purple
- 2D image but 3D if layer focal planes - Safranin dye counterstain
- Non-invasive – eye disease, endoscopic procedures - g- bacteria (thin walls) = red
- Florescence (absorb + reradiate) from dye - g+ bacteria susceptible to penicillin = inhibits cell wall
- Emit ↑ wavelength, filtered through pinhole aperture
- Only use light radiated close to focal plane, light from Acid fast technique
other planes ↓ resolution + blurring - Primary dye = all bacteria red
- Beam splitter (dichroic mirror) reflects laser + - Decolouriser acid = non-acid fast lose red
transmits reflected - Counterstain = non-acid fast turn blue
- Florescent tags for genes to see where travels in cell
Ultrastructure
Nucleus
- Contains DNA
- Controls metabolic activity
- Directs protein synthesis
- Nucleolus contains RNA + proteins = produce ribos
- Double mem nuclear envelope, prevent DNA damage
- Nuclear pores – where RNA molecules leave
I Plasma membrane
M A - Phospholipid bilayer (lipids + proteins)
- Regulate movement of substance (selective perm)
- Receptor molecules
Magnification = times larger the image is than actual
Resolution = ability to distinguish 2 points (detail) Mitochondria
- Limited by diffraction of light, reflections overlap - Matrix = internal enzyme fluid
- Smaller wavelength = higher resolution (electron) - Double membrane, cristae = folded inner membrane
- Mitochondrial DNA + ribosomes = own enzymes
Eyepiece divisions = stage micrometre / graticule divisions - Aerobic respiration – produce energy + ATP