Gregor Mendel
Father of modern genetics. Catholic priest. Observed his pea plants: how traits are passes down.
Mendel's 3 Law's.
Mendel's 3 Laws
1. Law of Dominance
2. Law of Segregation
3. Law of Independent Assortment
Law of Dominance (1st Law)
Genes have alleles in which some are more dominant than others.
Law of Segregation (2nd Law)
A heterozygois genotype has an equal chance of passing down the trait.
Law of Independent Assortment (3rd Law)
Double trait can cross over and match up as they wish.
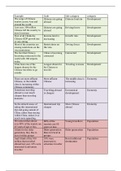
,DNA
Doxyribo Nucleic Acid; makes up chromosomes.
Gene
One segment/piece of a chromosome; controls the making of traits.
Dominant
Overpowering allele. Allele "A" is more dominant than allele "a."
Recessive
A gene that is overpowered by the dominant trait.
Genotype
Genes (letters) on alleles for a trait.
Phenotype
Physical expression of a trait.
Heterozygous
Different alleles.
, Homozygous
Same alleles
Allele
One form of a gene; you get 2 alleles, one from each parent.
Punnett Square
A table that shows how traits are passed down.
Multiple Alleles
More than one gene that's passed down.
Homologous
The same chromosome you got from each parent.