Lectures & articles
Week 1: 07/10/2024
HC1: Leadership in teams
A work team:
• 2 or more individuals
• Interdependent
o With respect to workflow, goals and/or outcomes
• Boundary management
o Different roles and responsibilities
• Shared goal
• Social interaction
o Face-to-face
o Increasingly
o Remotely
• Embedded in organizational system
o With boundaries and linkages to the broader system context and task
environment
When or why are teams (in)effective:
• Team effectiveness frameworks over time
o Finding a framework that help organize relevant factors into systematic
model than can be used to understand, predict, study and manage teams.
• Team processes versus emergent states
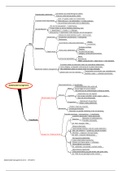
I-P-O-model (McGrath, 1964)
• Input
o Individual
o Group
o Environment
• Process
o Group interaction
• Output
o Performance
o Others
1
,IMOI-model (Ilgen, 2005)
• Input → knowledge diversity
o Individual
o Group
o Environment
• Mediator → information sharing
o Team processes:
interdependent team
activities that orchestrate taskwork in employees’ pursuit of goals. 3
processes:
▪ Transition → goal specification, strategy formulation
▪ Action → monitoring team goals and resources, coordinate
▪ Interpersonal → conflict management, motivation building
o Emergent states: cognitive motivational, and affective states of teams
that are typically dynamic in nature and vary as a function of team context,
inputs, processes and outcomes. More stable than processes. 3 states:
▪ Cognitive → shared mental models
▪ Motivational → team goal orientation, team efficacy
▪ Affective → trust, collective mood, psychological safety (be
yourself in the team)
• Output → team creativity
o Performance
o Others
• Input
2
,IPO-revisited to IMOI-models:
• ‘Process’ is not always a process
• Modelling the role of time
o Feedback loop
• Interactive effects and moderators
o Input → Knowledge diversity
▪ Leadership
▪ Autonomy
▪ Control
▪ Diversity
o Mediator → Information sharing
▪ Shared leadership
▪ Trust
▪ Monitoring
▪ Conflict
▪ Intragroup bias
o Output → Team creativity
▪ Team performance
▪ Leader performance
▪ Satisfaction
▪ Subgroup formation
▪ Team creativity
o Moderators
▪ Task complexity & interdependence
▪ Psychological safety
▪ Boundary spanning
▪ Method issues
▪ Team virtuality
Social loafing: reduced individual effort than other groupmembers.
Free riding: benefiting from the group's output without contributing at all. The thought
that your team is still effective without your help.
IMOI-framework in the course
• Moderators:
o Shared purpose
o Social support
o Voice
o Team heterogeneity
o Task interdependence
o Boundary spanning
3
, Team leadership: a process whereby an
individual influences a group of
individuals to achieve a common goal.
• Satisfying critical team needs to
enhance team effectiveness.
• But leadership theorizing is largely
conceptualized as individual and
leader centric.
• Towards a network of teams,
leadership is distributed, shared
and collective process that
involves effort on the part if all
group members, not just those in
leadership roles.
Morgeson examines leadership in teams more inclusively and team-centric:
• Move away from only studying formal team leaders
• Move away from single to multiple sources simultaneously
• Move away from static do dynamic leadership sources
Multiple sources of leadership: there are 2 or more people taking on leadership
functions. This can be either formally or informally, and internally or externally.
• A team with a formal external team leader that is additionally mentored
informally by a certified team coach.
Functional leadership theory (McGrath): the leadership role is to
do or get done, whatever is not being adequately handled for group
needs.
• Satisfying the critical team needs to enhance team
effectiveness
4