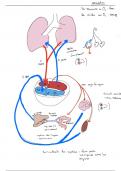
Nervous System Infections
- structure of nervous system
>neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus)
-
• types of nerves: sensory, motor, mixed, plexus (web-
like where nerves merge) • colonize mucosal surfaces of nasopharynx and
oropharynx
• brain
• transmission: respiratory droplet (highest among
- cerebrum: control voluntary muscles, perception, infants/adolescents), crowded living conditions
thinking • serotypes B, C, Y most common in US
- cerebellum: controls involuntary body movements
• adheres by fimbriae to nasopharyngeal mucosa
- brain stem: connect brain to spinal cord, control
breathing, heart rate, blood pressure • capsule protects from phagocytosis
• spinal cord • blebbing - sheds outer membrane, release
lipooligosaccharide, trigger inflammatory reaction
- nerve plexus, spinal ganglion, mixed spinal nerve, >
haemophilus influenzae
cauda equina • require NAD+ and heme for growth
• meninges
• colonize mucous membranes of upper respiratory
- dura mater: underneath bone tract
- arachnoid mater: middle layer • can cause: meningitis (mostly children, elderly),
- subarachnoid space: cavity between arachnoid and septicemia, pneumonia, pericarditis
pia mater, contain cerebrospinal fluid • virulence factors: capsule, IgA proteases, fimbriae,
- pia mater: layer close to spinal cord contain blood LPS
vessels that supply blood to brain and spinal cord - streptococcus pneumoniae
> blood brain barrier
• can cause: meningitis ( primarily under 5, elderly),
• cells serve as barrier to prevent entry of most pneumonia, sinusitis, otitis, bacteremia
microbes, large molecules • transmission: respiratory droplets
• specialized vessels deliver nutrient and oxygen to CNS • can colonize throat, lungs, sinuses, middle ear
• very small and lipophilic molecules can pass • bacteria can migrate to bloodstream, reach the
• bacteria require virulence factors, viruses have easier CNS
time invading • capsule protect from phagocytosis,
> CSF and Lumbar puncture
-
phosphorylcholine mediates cell adhesion in lungs,
• CSF serves as shock absorber, provides nutrients, meninges, vessels
electrolytes, oxygen to nervous tissue • toxins: hemolysis, IgA, protease, neurominidase,
• collected by lumbar puncture (spinal tap) hyaluronidase
- portals of infection - streptococcus agalactiae
• trauma, medical procedures, atonal transport in • normally colonize vaginal microbiota of pregnant
peripheral neurons women
• meningitis - microbes in blood/lymph penetrate BBB • vertical transmission during delivery
by infecting cells of meninges • neonatal meningitis (infants younger than 7 days)
-
bacterial meningitis - inflammation of meninges due to - prenatal screening: prophylactic administration
bacterial infection of penicillin
• S&S - sudden high fever, severe headache, NV, - listeria monocytogenes
drowsiness, confusion,lethargy, stiff neck, abnormal • frequently associated with outbreaks - fruits,
CSF values vegetables, dairy, poultry, processed meats
• can lead to encephalitis, deafness, blindness, coma, • refrigeration can't stop growth
death • primarily observed in neonates, pregnant women,
• if untreated, death can occur within 6 hours elderly, immunocompromised
• treated with IV antibiotics and corticosteroids • induce phagocytosis, escape phagocytes
• vaccines available to protect against N. meningitidis, • disease in pregnant women - spontaneous
S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae abortion, stillborn
• disease in newborn - intrauterine infection causing
meningitis in infant
- structure of nervous system
>neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus)
-
• types of nerves: sensory, motor, mixed, plexus (web-
like where nerves merge) • colonize mucosal surfaces of nasopharynx and
oropharynx
• brain
• transmission: respiratory droplet (highest among
- cerebrum: control voluntary muscles, perception, infants/adolescents), crowded living conditions
thinking • serotypes B, C, Y most common in US
- cerebellum: controls involuntary body movements
• adheres by fimbriae to nasopharyngeal mucosa
- brain stem: connect brain to spinal cord, control
breathing, heart rate, blood pressure • capsule protects from phagocytosis
• spinal cord • blebbing - sheds outer membrane, release
lipooligosaccharide, trigger inflammatory reaction
- nerve plexus, spinal ganglion, mixed spinal nerve, >
haemophilus influenzae
cauda equina • require NAD+ and heme for growth
• meninges
• colonize mucous membranes of upper respiratory
- dura mater: underneath bone tract
- arachnoid mater: middle layer • can cause: meningitis (mostly children, elderly),
- subarachnoid space: cavity between arachnoid and septicemia, pneumonia, pericarditis
pia mater, contain cerebrospinal fluid • virulence factors: capsule, IgA proteases, fimbriae,
- pia mater: layer close to spinal cord contain blood LPS
vessels that supply blood to brain and spinal cord - streptococcus pneumoniae
> blood brain barrier
• can cause: meningitis ( primarily under 5, elderly),
• cells serve as barrier to prevent entry of most pneumonia, sinusitis, otitis, bacteremia
microbes, large molecules • transmission: respiratory droplets
• specialized vessels deliver nutrient and oxygen to CNS • can colonize throat, lungs, sinuses, middle ear
• very small and lipophilic molecules can pass • bacteria can migrate to bloodstream, reach the
• bacteria require virulence factors, viruses have easier CNS
time invading • capsule protect from phagocytosis,
> CSF and Lumbar puncture
-
phosphorylcholine mediates cell adhesion in lungs,
• CSF serves as shock absorber, provides nutrients, meninges, vessels
electrolytes, oxygen to nervous tissue • toxins: hemolysis, IgA, protease, neurominidase,
• collected by lumbar puncture (spinal tap) hyaluronidase
- portals of infection - streptococcus agalactiae
• trauma, medical procedures, atonal transport in • normally colonize vaginal microbiota of pregnant
peripheral neurons women
• meningitis - microbes in blood/lymph penetrate BBB • vertical transmission during delivery
by infecting cells of meninges • neonatal meningitis (infants younger than 7 days)
-
bacterial meningitis - inflammation of meninges due to - prenatal screening: prophylactic administration
bacterial infection of penicillin
• S&S - sudden high fever, severe headache, NV, - listeria monocytogenes
drowsiness, confusion,lethargy, stiff neck, abnormal • frequently associated with outbreaks - fruits,
CSF values vegetables, dairy, poultry, processed meats
• can lead to encephalitis, deafness, blindness, coma, • refrigeration can't stop growth
death • primarily observed in neonates, pregnant women,
• if untreated, death can occur within 6 hours elderly, immunocompromised
• treated with IV antibiotics and corticosteroids • induce phagocytosis, escape phagocytes
• vaccines available to protect against N. meningitidis, • disease in pregnant women - spontaneous
S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae abortion, stillborn
• disease in newborn - intrauterine infection causing
meningitis in infant