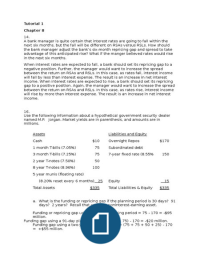
Rational Expressions: Multiplication And Division
E.g.1. 9x2 - 4 / 6x2 - 7x + 2 = (3x - 2)(3x + 2) x (2x - 1)(x + 5) = 3x + 2
2x2 - 4x - 70 2x2 + 9x - 5 (2x - 14)(x + 5) (3x - 2)(2x - 1) 2(x - 7)
E.g.2. 4x2 - 9 x x2 - 25 = (2x - 3)(2x + 3) x (x +5)(x - 5) = x-5
2 2
2x + 13x + 15 2x - 5x + 3 (2x + 3)(x + 5) (2x - 3)(x - 1) x-1
E.g.3. 2x2 + x - x2 - 13x + 20 = (2x - 5)(x + 3) x x(x - 4) = x+3
x x2 - 4x x (2x - 5)(x - 4)
Rational Expressions: Addition And Subtraction
E.g.1. 1 - 2 + x - 15 = x2 - 25 - 2(x - 5) + x - 15 , as x2 - 25 is the lowest common factor.
x+5 x2 - 25 x2 - 25
= x2 - x - 30 = (x + 5)(x - 6) = x-6
x2 - 25 (x + 5)(x - 5) x-5
E.g.2. 1 = 1 = 2x , cross-multiplying, as there is no common factor.
1+1 x+2 2+x
x 2 2x
E.g.3. 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = x-4 ,
3 -1 3 - x-4 3 - 1(x - 4) 7-x 7-x
x-4 x-4 x-4 x-4 x-4
E.g.4. 3x + 5 - 2x - 1 = (3x + 5)(x - 1) -(2x - 1)(x + 1) = 3x + 5 - 2x + 1 = x+6
(x + 2)(x + 1) (x + 2)(x - 1) (x + 2)(x + 1)(x - 1) x+2 x+2
Here, a common factor is found & the fractions multiplied by what they need to be to have the common
factor. Remember that if there’s a common factor, simply multiply the numerators. If not, or there’s a
mixture, times the fractions by what you need to until there is.
E.g.5. x + 11 - 4 = x + 11 - 4 = x2 + 11x - 4x + 12 = x2 + 7x + 12 ,
x2 - 9 x2 + 3x (x - 3)(x + 3) x(x + 3) x(x + 3)(x - 3) x(x + 3)(x - 3)
= (x + 3)(x + 4) = x+4
, x(x + 3)(x - 3) x(x - 3)
Rational Expressions: More Difficult Division
E.g.1. 2x2 + x - 4 = (x - 1)(2x + 3) - 1 = 2x + 3 - 1 . You have to make the numerator a
x-1 x-1 x - 1 factor of (x - 1), add remainders if
they are needed, then divide out.
E.g.2. 6x3 - 4x2 - 3x - 5 = (2x2 - 1)(3x - 2) - 7 , as to get from 2 to -5, you -7. = 3x - 2 - 7 .
2x2 - 1 2x2 - 1 2x2 - 1
Ranges & Domains
Domain Range
1 3
2 5 The function for this range, with their range (answers when put in to the function of
3 7 x) is 2x + 1. A domain = the inputs, the range = the outputs. Ranges are of f(x),
4 9 not just x. Note - Even function: f(-x) = f(x) and an Odd function: f(-x) = -f(x).
One - One Mapping
f(x) = x2, x > 0. f(x) = ±√x, x < 3.
This is one-one mapping, as This isn’t one-one mapping,
there is only one y value for as there are 2 y values for
each corresponding x value. each corresponding y value.
Notice that there’s a black Notice there’s an unfilled
dot, which shows where the dot, showing where the
curve’s been cut. curve’s cut, as it’s >, not >.
f(x) = x - 3, -1 < x < 10. f(x) = √x + 2, x > 0.
Notice again the black Another unfilled < dot.
point, showing where the Unnecessary really, as
curve is cut off. It is filled no values of x are < 0.
because it is <, not <, as F(x) may be written in
with inequalities. these as f:x→√x + 2.
One-One & Many-One
E.g.1. y = x3. This is a one-one, E.g.2. y = x2, -3 < x < 2. E.g.3. A square is cut out of this square.
as no ranges are the same. So this is a many-one. Find a domain for function A. A = 144 – x2
So the min value for x is 0. Using
Pythagoras: the max value for x = √72.
Domain = 0 < x < 6√2.
E.g.3 A function is defined by h: x → cosx, 0 < x < π. Is this a one-many or one-one function?