Resume
Samenvatting alle hoorcolleges B&C2
- Cours
- Établissement
- Book
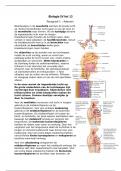
Een samenvatting van alle hoorcolleges van de cursus Brein en Cognitie 2 in het tweede jaar van de bachelor Psychologie aan de Radboud Universiteit. In het Engels geschreven. Bevat de volgende onderwerpen: Korsakoff, Vasculaire implantaten, epilepsie, Alzheimer, Parkinson, MS en rehabilitatie.
[Montrer plus]