Hard discounters
Retail Disruptors (book) by J.B. Steenkamp & L. Sloot Chapter 1, Chapter 2, Chapter 3. Chapter 6,
Chapter 7
Hard discounter retailers
Offer basic goods at the lowest possible prices while maintaining high-quality standards
Reduce costs by
o displaying items on shipping pallets and in boxes in which they arrive
o minimally decorated stores
o offer limited assortment which enables to provide high volumes of basic goods
o streamline operations
Few options (SKU’s) per category results in easy decision-making
Hard discounters offer simplicity. Brand simplicity = brands that are easy to understand,
transparent and honest and make consumers feel valued.
Ensure high quality
Why hard discounters become attractive for middle / high class consumers
Stagnating incomes
Impact of recessions: customers switched to HD and did not return after recession
Smart shopping phenomenon: “smart shopping” to purchase goods at low price
The hard discounter business model
The four key success factors of hard discounters:
1. High volume per SKU
2. Irresistible value for money
3. High profitability
4. Rapid expansion of store network
These key success factors are interrelated and support each other, making it hard to imitate
Hard discounters distinguish themselves compared to regular grocery retailers with: 1.) very limited
assortment, 2.) strong focus on private labels, 3.) small and “spartan-like” stores, 4.) unbeatable price
quality. They are in developing in terms of modern stores, increased choices in fresh products, fresh
baked bread, more organic and fair trade etc.
,Differences between hard discounters
Hard discounters differ from each other according to the private-label strategy pursued
Aldi – the inventor of the hard discount concept
o “Getting the best value for money”
o Aldi Nord (= slower to modernize, more appealing store concept) vs. Aldi Sud (=
quicker to innovate, move with times, early in expanding its product range in line with
consumer’s needs)
o Five pillars: 1.) ultra-limited assortment, 2.) unwavering focus on cost avoidance,
3.) unique private-label strategy, 4.) decentralized organization, 5.) company culture
dedicated to simplicity
o ANIKO program (Aldi Nord Instore Konzept) is modern stores with increased choice
in vegetables and fruits etc. to become quality discounter
Lidl – the only firm Aldi fears
o Lidl copied the large success of Aldi’s discount concept
o Similarities with Aldi: display products in delivery cartons, small stores, basic
ambience, good quality, low prices, private-label assortment, limited-time offers to
drive store traffic
o Likely to become the world’s number one hard discounter: 1.) international
expansion, 2.) organizational structure, 3.) assortment strategy, 4.) marketing
programmes
Trader Joe’s – the upscale hard discounter
o Owned by Aldi Nord but independently operated
o “Trader Joe’s customer experience”
o Mainly sell private label products under the banner name
o Little marketing expenditures
o Unique positioning and assortment and in-store experience
DIA – the convenience hard discounter
o Lidl is seen as their main competitor
o Offer more national brands in each category to give consumers more choice
o Stores are located on premium locations
o 2PF business model:
1.) Proximity: neighbourhood locations offer customers easy access
2.) Price: DIA’s price image is more favourable than the actual price adv.
3.) Franchising: franchises provide work for whole family
Implications of hard discounter entry on different types of conventional retailers
Five types of conventional retail formats
1. Premium retailers
Wide and deep assortment of SKUs
Additional services
Shopping experience is central (well-trained staff)
Price level higher than average
Experienced a growth in market share after hard discounter entry
2. Mainstream retailers
Largest share of the grocery market in terms of sales
Modest to good in terms of assortment, quality, and service
Decent price-quality
EDLP approach (low price, few promo) or HiLo strategy (frequently
promotions)
No difference in market share loss between HiLo and EDLP when discounter
arised
But the entrance of hard discounter resulted in a 10 % loss in market share
3. Warehouse clubs
Large stores with large assortment
, Package sizes are typically large
Often membership card needed to enter the store
Visit stores infrequently but average spent is $200 per trip
4. Brand discounters
Low prices with limited assortment of leading national brands
Create “blue ocean” by entering uncontested market space
Shopping experience is utilitarian
5. Proximity retailers
Convenience stores
Limited variety of grocery products at relatively high prices
Less affected by hard discounters
Retail formats can be classified based on perceived price and perceived added value in retail market
space map. The retailing space can be divided into commodity market (e.g. aldi, lidl), mid-market
(e.g. jumbo, AH), specialty market (e.g. Waitrose, wholefoods).
Hard discounters (e.g. brand discounters) impact the shopper’s mindset
1. Change in reference price (e.g. result in lower reference price; reluctance to pay high price)
2. Hard discounter devaluation process means that value-related attributes (e.g. service level,
well-trained employees, large assortment) are less important than price-related attributes
3. Contrast effect means that conventional retailers are perceived more positively on added-
value attributes but the price image of the conventional retailer declines. But, less importance
is attached to added-value attributes as hard discounter enter the area.
The hard discounter devaluation process and contrast effect create double jeopardy for conventional
retailers.
Initial reactions toward hard discounters
1. Neglect no worries
2. Derogation stage discounters embraced, retailer publicly downplay them
3. Panic phase panic starts when large market portion is taken, cut prices
4. Coordinated response develop balanced strategy to highlight strengths to survive
Four strategic reactions to hard discounter encroachment
Defensive Fight-back strategy Downgrading strategy
Most applicable for - Reduce prices (head-to-head - lowering overall price level while
price-focused / competition) by providing a range of cutting costs by reducing assortment,
EDLP mainstream low-price options and lower prices of staff levels & (online) services
retailers and existing assortment - more robust strategy than fight-
warehouse clubs - Dominant approach in panic phase back strategy
, Offensive Value-improvement strategy Value-redefinition strategy
Most applicable for - Offering more value by adding - Aggressive offensive strategy
service-focused extra services, improve goods, more - Retailer tries to lead the field by
HiLo mainstream convenience, or higher quality redefining what is great value
retailers and - Concept improvement and early - Expanding the market space
premium retailers. adopters of innovations outward in terms of price and value.
- Scan market for trends and study - Improve assortment completeness
competing retailers’ initiatives and quality while at the same time
improve customer services
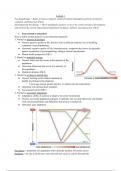
Bell-curve / normally distributed retail market
“Wish line”: consumers prefer local, organic, high quality, fair trade, convenience etc.
“Wish to pay”: we want added value but we do not want to pay for this, want low price
Combining wish line with wish to pay line results in normally distributed market
o Therefore, most retailers are situated in the middle
o Mid market = 50 – 75% of market
o Commodity = 10 – 30 % of market
o Specialty = 5 – 15 % of market
Mid-markets experience threats from both sides (e.g. commodity and specialty) causing hyper
competition
Well curve = flipped bell curve showing the growth potential. Mid-market has lowest growth
potential. Hard discounters and technologically advanced stores push back the mid-market.
Average rotation per item per week
Average rotation hard discounter = 50, compared to 5 for conventional retailer
€180.000 per store per week / €1,80 average price / 2.000 products = 50
€240.000 per store per week / €2,40 average price / 20.000 products = 5
The hard discounter business model
Three main drivers of competitive sustainable advantage
1. Efficient retail operation low HQ cost, store efficiency, smart packing
2. Knowledgeable & efficient procurement limited items, large volume, deep knowledge of supply