Exam (elaborations)
Maryville 612 Exam 1 QUESTIONS WITH 100 % VERIFIED CORRECT ANSWERS A+ GRADED
- Institution
- Maryville University Of St. Louis
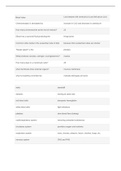
Maryville 612 Exam 1 QUESTIONS WITH 100 % VERIFIED CORRECT ANSWERS A+ GRADED Claudication - ANS a condition in which cramping pain in the leg is induced by exercise, typically caused by obstruction of the arteries. May be characterized as a dull ache with accompanying muscle fatigue and cramps...
[Show more]