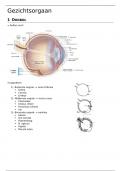
DPS – 2015 – AN INTRODUCTION TO ENVIROMENTAL EDUCATION
1.0 EDU 122 – ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION
1.1 Understanding key concepts related to environmental education.
- What is environment – Simply stated environment is that which surrounds
us. The word itself derives from the French term ‘environ’ that means the
surrounding;
(1) Muyanda Mutebi (1993) defines environment as the surrounding
conditions that influence the behavior and growth development of living
things.
(2) Lucie Sauve (2) – Environment is a fabric of woven threads and an
interface between nature and culture.
(3) Dichil (quoted by Fiew 1993) defines environment as interactions
between physical surroundings and social, political and economic forces
that organizes us in the context of these surroundings e.t.c.
Environment therefore can be conceived as a sum total of natural, artificial and socio
components of the material world which are in direct interaction with human kind utilizing
controlling harnessing and influencing adapting.
Environment, according to O’donoghue, is a four dimensional social construct as shown below;
(i) Biophysical – referring to living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) simply meaning the
life and the life support systems.
(ii) Social systems – includes humans and their cultural interactions as diverse groups.
(iii) Economic – refers to man’s / Human economic endeavors to sustain himself in the
environment.
(iv) Political – Refers to Political power, Policy, political decisions and all other legal
factors that determine the access and distribution of natural resources – governance.
In essence, environment will have no reality without human beings. Environment is also
perceived by people differently depending on their habitatious cf. inhabitants of Tundra,
Tropical lands, Equatorial lands, the hot deserts etc. all will have very different views of the
environment.
Page
1
,Environment Pictorially represented:-
Political
Social
Environment Econoicc
Biophysical
Faural flora + physical
NB: The dynamic interrelationship of the four social dimensions of environment (O’Doughue)
The environment in its totality provides mankind with the resources for his very survival - this
is done through the vital life sustaining activities such as cultivating, grazing, sheltering,
hunting and gathering, drinking, breathing e.t.c. It would be interesting to note urban and rural
settlements are both part & parcel of the environment.
NB: The environment does not belong to people; rather people belong to the environment. So,
whatever befalls the environment befalls people also cf. Global warming environment has no
fixed boundaries as it extends all-round the planet earth. The man-made environmental
demarcations are only for purposes of convenience.
1.2 Environmental Education
- O’Doughou – Environmental Education is communications process that causes
behavioral changes in human beings towards the environment.
- The Australian Association for environmental education (AAEE) says that environment
education is across the curriculum approach to learning that helps the individuals to
understand the environment to understand the environment with the ultimate aim of
developing a caring and committed attitude that will foster the desire and ability to act
responsibility in the environment.
- Environmental Education is concerned with knowledge, feelings, attitudes, skills,
values, social & community actions – thus it affects also people’s way of thinking and
perception.
- Muganda – Mutebi (1993) says that Environmental Education is a process of learning
and teaching knowledge and skills that enable us to understand and appreciate our
environment and the inter relatedness between us, our cultures and environmental
resources.
Page
2
,Simply said, environmental education can therefore be conceptualized as a process through
which;
(i) Learners acquire knowledge, skills, attitudes, values on environmental issues.
(ii) The knowledge so acquired improves the awareness about the status of different
environments.
(iii) This awareness stimulates concerns and strong feelings about quality of the
environment on focus
(iv) These strong feeling and concern above leads to a committement in wanting to
improve and conserve the environment.
(v) And this commitment desire calls for participation and action in order to solve some
of the environmental problems.
Environmental Education is therefore the strongest and most effective tool/means used in
solving environmental problems. Other tools include environmental law; Environmental
managers, environmental community workers, engineers economists, foresters game hardens,
Policy makers e.t.c.
The rational for teaching environmental education to prospective teachers;
- Teachers live and work in an environment and are part and parcel of this
environment will have either positive or negative impacts depending on how
they go about it.
- Teachers are role models to their learners besides imparting the knowledge
skills and attitudes values that relate to the management and conservation of
the environment.
- Teachers are role models to the immediate School Society in addition to being
opinion leaders in those communities. Their influence in making decisions
involving environmental matters cannot be underestimated.
- Teachers’ influence on Societies has a multiple effect on the populations
through their learners and Pupil movement.
1.30 Approaches Used To Teach Environmental Education
These are the multidisciplinary and the interdisciplinary. The former is more applicable during
the formulative / early years of the life of the learner, while the latter approach is more
commonly used as higher education is approached.
1.31 The Multidisciplinary Approach
Environmental contents are infused into disciplines / subjects that are taught in School e.g
Geography, Science History Literature, Social Ethics e.t.c. this approach is not cumbersome to
curriculum developers as o extra subject for the timetable is necessary. Again no specialized
teaching and learning resources are required. The approach is also cheap to effect but is not
Page
3
, capable of sensitizing the learners adequately in matters of environment. The deliberate and
constant co-ordination and awareness may not be fully developed in all teachers. The approach
as pointed earlier, can be used in Primary Schools, Secondary Schools Training Colleges and
some faculties / departments in tertiary institutions.
Chemistry
Gases Religion
History Cleanliness is second to
Origin of management godliness; concept of good
practices over time sanitation, moral and ethical
trends in pollution concern over garbage.
Mathematics
Biology Qualities of waste
Impact of pollutants on Pollution on generated percentage of
food chains Biodegradable Environmental people affected by each
pollutants
Issue category of waste.
Technology Economics
Appropriate technologies Cost- Benefit analysis of
to manage pollutants for pollution effect. Polluter –
cleaner production pay Principle Pollution effect
on GDP
Agriculture
Inorganic fertilizers,
pesticides, herbicides
insecticides, fungicides
Multidisciplinary approach of teaching the topic “Pollution” in a School.
NB:- The multidisciplinary approach of teaching environmental issues requires that the
teachers are quite conscious of what they intend to teach; fo it deliberately and honestly while at
the same time relating their subject of focus to the environmental issues. Curriculum
developers too will need to ensure that different topics on environmental issues are sliced
among the subjects existing in the School Curriculum taught in Schools.
1.32 The Interdisciplinary Approach of teaching Environment
This approach allows environmental education to be taught in Schools as a Subject in its own
right; often included in the block timetable. Teachers will need to be equipped with special
methods of teaching subject and specially designed the teaching / learning materials are
provided. The approach is somehow expensive on the part of hiring teachers and the
production of teaching / learning materials. It is however more effective in changing the
learners attitudes, behavior, lifestyles and in making them environmentally friendly. It is the
Page
4
1.0 EDU 122 – ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION
1.1 Understanding key concepts related to environmental education.
- What is environment – Simply stated environment is that which surrounds
us. The word itself derives from the French term ‘environ’ that means the
surrounding;
(1) Muyanda Mutebi (1993) defines environment as the surrounding
conditions that influence the behavior and growth development of living
things.
(2) Lucie Sauve (2) – Environment is a fabric of woven threads and an
interface between nature and culture.
(3) Dichil (quoted by Fiew 1993) defines environment as interactions
between physical surroundings and social, political and economic forces
that organizes us in the context of these surroundings e.t.c.
Environment therefore can be conceived as a sum total of natural, artificial and socio
components of the material world which are in direct interaction with human kind utilizing
controlling harnessing and influencing adapting.
Environment, according to O’donoghue, is a four dimensional social construct as shown below;
(i) Biophysical – referring to living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) simply meaning the
life and the life support systems.
(ii) Social systems – includes humans and their cultural interactions as diverse groups.
(iii) Economic – refers to man’s / Human economic endeavors to sustain himself in the
environment.
(iv) Political – Refers to Political power, Policy, political decisions and all other legal
factors that determine the access and distribution of natural resources – governance.
In essence, environment will have no reality without human beings. Environment is also
perceived by people differently depending on their habitatious cf. inhabitants of Tundra,
Tropical lands, Equatorial lands, the hot deserts etc. all will have very different views of the
environment.
Page
1
,Environment Pictorially represented:-
Political
Social
Environment Econoicc
Biophysical
Faural flora + physical
NB: The dynamic interrelationship of the four social dimensions of environment (O’Doughue)
The environment in its totality provides mankind with the resources for his very survival - this
is done through the vital life sustaining activities such as cultivating, grazing, sheltering,
hunting and gathering, drinking, breathing e.t.c. It would be interesting to note urban and rural
settlements are both part & parcel of the environment.
NB: The environment does not belong to people; rather people belong to the environment. So,
whatever befalls the environment befalls people also cf. Global warming environment has no
fixed boundaries as it extends all-round the planet earth. The man-made environmental
demarcations are only for purposes of convenience.
1.2 Environmental Education
- O’Doughou – Environmental Education is communications process that causes
behavioral changes in human beings towards the environment.
- The Australian Association for environmental education (AAEE) says that environment
education is across the curriculum approach to learning that helps the individuals to
understand the environment to understand the environment with the ultimate aim of
developing a caring and committed attitude that will foster the desire and ability to act
responsibility in the environment.
- Environmental Education is concerned with knowledge, feelings, attitudes, skills,
values, social & community actions – thus it affects also people’s way of thinking and
perception.
- Muganda – Mutebi (1993) says that Environmental Education is a process of learning
and teaching knowledge and skills that enable us to understand and appreciate our
environment and the inter relatedness between us, our cultures and environmental
resources.
Page
2
,Simply said, environmental education can therefore be conceptualized as a process through
which;
(i) Learners acquire knowledge, skills, attitudes, values on environmental issues.
(ii) The knowledge so acquired improves the awareness about the status of different
environments.
(iii) This awareness stimulates concerns and strong feelings about quality of the
environment on focus
(iv) These strong feeling and concern above leads to a committement in wanting to
improve and conserve the environment.
(v) And this commitment desire calls for participation and action in order to solve some
of the environmental problems.
Environmental Education is therefore the strongest and most effective tool/means used in
solving environmental problems. Other tools include environmental law; Environmental
managers, environmental community workers, engineers economists, foresters game hardens,
Policy makers e.t.c.
The rational for teaching environmental education to prospective teachers;
- Teachers live and work in an environment and are part and parcel of this
environment will have either positive or negative impacts depending on how
they go about it.
- Teachers are role models to their learners besides imparting the knowledge
skills and attitudes values that relate to the management and conservation of
the environment.
- Teachers are role models to the immediate School Society in addition to being
opinion leaders in those communities. Their influence in making decisions
involving environmental matters cannot be underestimated.
- Teachers’ influence on Societies has a multiple effect on the populations
through their learners and Pupil movement.
1.30 Approaches Used To Teach Environmental Education
These are the multidisciplinary and the interdisciplinary. The former is more applicable during
the formulative / early years of the life of the learner, while the latter approach is more
commonly used as higher education is approached.
1.31 The Multidisciplinary Approach
Environmental contents are infused into disciplines / subjects that are taught in School e.g
Geography, Science History Literature, Social Ethics e.t.c. this approach is not cumbersome to
curriculum developers as o extra subject for the timetable is necessary. Again no specialized
teaching and learning resources are required. The approach is also cheap to effect but is not
Page
3
, capable of sensitizing the learners adequately in matters of environment. The deliberate and
constant co-ordination and awareness may not be fully developed in all teachers. The approach
as pointed earlier, can be used in Primary Schools, Secondary Schools Training Colleges and
some faculties / departments in tertiary institutions.
Chemistry
Gases Religion
History Cleanliness is second to
Origin of management godliness; concept of good
practices over time sanitation, moral and ethical
trends in pollution concern over garbage.
Mathematics
Biology Qualities of waste
Impact of pollutants on Pollution on generated percentage of
food chains Biodegradable Environmental people affected by each
pollutants
Issue category of waste.
Technology Economics
Appropriate technologies Cost- Benefit analysis of
to manage pollutants for pollution effect. Polluter –
cleaner production pay Principle Pollution effect
on GDP
Agriculture
Inorganic fertilizers,
pesticides, herbicides
insecticides, fungicides
Multidisciplinary approach of teaching the topic “Pollution” in a School.
NB:- The multidisciplinary approach of teaching environmental issues requires that the
teachers are quite conscious of what they intend to teach; fo it deliberately and honestly while at
the same time relating their subject of focus to the environmental issues. Curriculum
developers too will need to ensure that different topics on environmental issues are sliced
among the subjects existing in the School Curriculum taught in Schools.
1.32 The Interdisciplinary Approach of teaching Environment
This approach allows environmental education to be taught in Schools as a Subject in its own
right; often included in the block timetable. Teachers will need to be equipped with special
methods of teaching subject and specially designed the teaching / learning materials are
provided. The approach is somehow expensive on the part of hiring teachers and the
production of teaching / learning materials. It is however more effective in changing the
learners attitudes, behavior, lifestyles and in making them environmentally friendly. It is the
Page
4