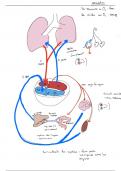
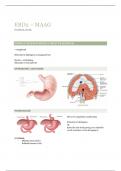
Rio Salado Bio201 exam 1
levels of structural organization that make up the human body - atom, molecule, bio molecule,
organelle, cells, tissues, organ, organ system, organisms
skeletal system - Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to
support movement. Made up of bones and joints
reproductive system - Reproduce offspring- produce male sex cells (sperm) and female sex cells
(oocytes)
Muscular System - Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression.
Maintains posture, and produces heat.
endocrine system - the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete
hormones into the bloodstream
integumentary system - Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail, protects
Respritory system - Keeps blood supplied with oxygen and removes CO2.
cardiovascular system - Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients,
wastes, etc. The heart pumps blood.
urinary system - Cleanses the blood. Rids the body of wastes. Maintains salt and water balance.
digestive system - Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body
cells.
,nervous system - the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve
cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
lymphatic system - Composed of a network of vessels, ducts, nodes, and organs. Provides defense
against infection.
positive feedback mechanisms - Feedback that tends to cause the level of a variable to change in the
same direction as an initial change
negative feedback mechanisms - the net effect of the response to the stimulus is to shut off the original
stimulus or reduce its intensity
homeostatic imbalance - a disturbance in homeostasis resulting in disease
anatomy - The study of body structure
physiology - The study of body function
anatomical position - To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward
anterior - front of the body
posterior - back of body
superficial - near the surface
deep - away from the surface
, superior - above
inferior - below
medial - toward the midline
lateral - away from the midline
proximal - Closer to the point of attachment
distal - away from the point of attachment
supine - lying on the back
prone - lying face down
coronal - divides the body into slices from front to back
sagittal - A plane that divides the body into right and left portions.
transverse - Divides body into upper and lower parts
dorsal - back
levels of structural organization that make up the human body - atom, molecule, bio molecule,
organelle, cells, tissues, organ, organ system, organisms
skeletal system - Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to
support movement. Made up of bones and joints
reproductive system - Reproduce offspring- produce male sex cells (sperm) and female sex cells
(oocytes)
Muscular System - Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression.
Maintains posture, and produces heat.
endocrine system - the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete
hormones into the bloodstream
integumentary system - Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail, protects
Respritory system - Keeps blood supplied with oxygen and removes CO2.
cardiovascular system - Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients,
wastes, etc. The heart pumps blood.
urinary system - Cleanses the blood. Rids the body of wastes. Maintains salt and water balance.
digestive system - Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body
cells.
,nervous system - the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve
cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
lymphatic system - Composed of a network of vessels, ducts, nodes, and organs. Provides defense
against infection.
positive feedback mechanisms - Feedback that tends to cause the level of a variable to change in the
same direction as an initial change
negative feedback mechanisms - the net effect of the response to the stimulus is to shut off the original
stimulus or reduce its intensity
homeostatic imbalance - a disturbance in homeostasis resulting in disease
anatomy - The study of body structure
physiology - The study of body function
anatomical position - To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward
anterior - front of the body
posterior - back of body
superficial - near the surface
deep - away from the surface
, superior - above
inferior - below
medial - toward the midline
lateral - away from the midline
proximal - Closer to the point of attachment
distal - away from the point of attachment
supine - lying on the back
prone - lying face down
coronal - divides the body into slices from front to back
sagittal - A plane that divides the body into right and left portions.
transverse - Divides body into upper and lower parts
dorsal - back