P6 Unit 3 Boaz Spaan
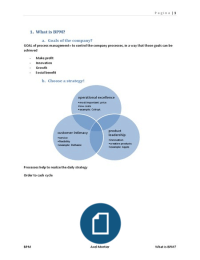
What is the marketing mix?
The marketing is an good framework for developing marketing plans. The marketing mix for physical
goods is generally accepted as being made up of four P’s. this P’s are: Product, Price, Promotion and
Place. Once the marketing objectives have been agreed marketing plans must be developed to achieve
the goals of the business.
Product, Price, place and promotion
A product is anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a want or need. Products include physical
goods, services, experiences, events, persons, places, properties, organisations, information and ideas.
Price is the amount of money consumers have to pay to acquire the product. This can vary considerably.
place describes where and how the consumer can obtain the product. Tesco has stores all over the
country but place does not have to be a physical location. Nowadays consumers can buy books over the
telephone, via the internet or through their TV remote control. Producers have to choose the best
method carefully to ensure consumers can find their product in an appropriate place when they decide
to make a purchase. Promotion describes the activities undertaken to ensure the consumer knows about
the product and its capabilities. It usually combines advertising, sales promotion, public relations and
personal selling.
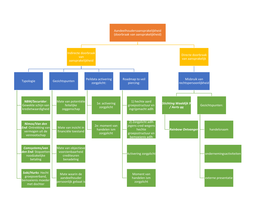
What is the product life cycle curve?
The product life cycle concept reflects the theory that products, like people, live a life. They are born,
they grow up, they mature and eventually they die. It is a useful concept for thinking about what a
product has achieved and where it is heading in the future.
Seven P’s strategies
Premium pricing, keeps the price high to ensure the good quality of the product
penetration pricing, short term strategy, keeps the prices low and then it increases
skim pricing, the prices are going from high to low.
Psychological pricing, it look cheaper but it isn’t. for example 5,99 it looks 5 euros but it is 6.
captive product pricing, the purchase of the product is low, but all the accessories are high in price.
product line pricing, pricing of different products within the same product range at different price
points.
Economy pricing, the deliberate setting of a low price in order to boost sales.
What is the marketing mix?
The marketing is an good framework for developing marketing plans. The marketing mix for physical
goods is generally accepted as being made up of four P’s. this P’s are: Product, Price, Promotion and
Place. Once the marketing objectives have been agreed marketing plans must be developed to achieve
the goals of the business.
Product, Price, place and promotion
A product is anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a want or need. Products include physical
goods, services, experiences, events, persons, places, properties, organisations, information and ideas.
Price is the amount of money consumers have to pay to acquire the product. This can vary considerably.
place describes where and how the consumer can obtain the product. Tesco has stores all over the
country but place does not have to be a physical location. Nowadays consumers can buy books over the
telephone, via the internet or through their TV remote control. Producers have to choose the best
method carefully to ensure consumers can find their product in an appropriate place when they decide
to make a purchase. Promotion describes the activities undertaken to ensure the consumer knows about
the product and its capabilities. It usually combines advertising, sales promotion, public relations and
personal selling.
What is the product life cycle curve?
The product life cycle concept reflects the theory that products, like people, live a life. They are born,
they grow up, they mature and eventually they die. It is a useful concept for thinking about what a
product has achieved and where it is heading in the future.
Seven P’s strategies
Premium pricing, keeps the price high to ensure the good quality of the product
penetration pricing, short term strategy, keeps the prices low and then it increases
skim pricing, the prices are going from high to low.
Psychological pricing, it look cheaper but it isn’t. for example 5,99 it looks 5 euros but it is 6.
captive product pricing, the purchase of the product is low, but all the accessories are high in price.
product line pricing, pricing of different products within the same product range at different price
points.
Economy pricing, the deliberate setting of a low price in order to boost sales.