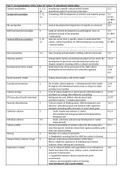
Cultural socialization 1, 3, 9, Introducing a specific cultural world/context 1) 3
28 Intentional explicit transmission/education
Comparative paradigm 1, 11, Comparing child development of minority and majority groups 1) 2
14 (ex. Physical discipline in immigrants is disfunctional) 3) 553
6) 1893,
1894
Etic perspective 1 Look at developmental trajectories of majority as universal 1) 2
Deficit perspective/paradigm 1 Looks at minority development as pathological, focus on 1) 2
problems instead of the potential 6) 1894
= dysfunction
Cultural difference paradigm 1, 11, Uses the norms from a specific culture to understand this 1) 2
14 culture, cultural specificity of child development & parenting 6) 1895
= dysnormativity
(ex. Immigrants have practices of discipline, we can’t assume
that our norms our the measure, we see it as disnormative)
Emic perspective 1-2 Uses meaning and parameters withing cultural community 1) 2
Meaning systems Interpretative frames and behavioral patterns from which the 1) 5-6
development trajectories and educational practices are
shaped and given meaning within a cultural community
Developmental niche model 2 Determines how micro-processes in the child’s direct 1) 6-7
developmental environment are culturally regulated 3) all
4) 2
Social-economic model / Culture doesn’t play a role in this model 3) 552
Ecocultural perspective 2 Set of daily cultural patterns → developmental niche model 2) all
Ecological and institutional factors have an impact on daily 4) 2
activities from families
Cultural ecology 2 A set of cultural patterns in which parent-child interaction is 2) 277
inscribed, an ecology that influences everything
EFI (ecocultural family interview) Asking parents and children directly about daily 2) 277
activities/routines + includes observation
Parental ethnotheories 3 Cultural models of thinking about child development and 1) 6-7
behavior, educational goals and opinions with regard the
adequate parenting skills necessary to reach these goals
Collective cultures 3 - Goals: loyalty and cohesion (= static) 4) 2,4
- Intra-familial and intergenerational interdependence
- Relational self
Individual cultures 3-4 - Goals: autonomy and personal development (=static) 4) 2,4
- Separated self
Culture conflict / Universal desirability of western values for the young and a 4) 3,
view that parents maintain entrenched, ageless positions with
little new understanding
Shomaj 4 Members of a cultural community
→ Bangladesh: ensuring that the child has a place in shomaj
‘Disease-illness-sickness’ triade 5 Disease: professional interpretation of the illness
Illness: subjective experience of individual and context
Sickness: illness withing the community
Explanatory models 6 A set of coherent beliefs and expectations at an individual or 1) 8
family level about the cause, indices, course, treatment and
outcome of dysfunction
→ negotiation between those involved and social
environment
= diverse and changeable matrix of meaning
THIS DOMINANT USE IS QUESTIONED