- The most important macroeconomic variable is GDP because it measures both the nation’s
total output and total income
- The greater the GDP, the greater the way of living
- But this does not mean that all are happy with their ways of living
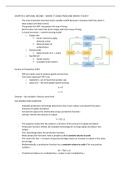
- A closed economy -> market clearing model
o Supply side
Factor markets (supply,
demand, price)
Determination of
output/input
o Demand side
Determinants of C, I, and G
o Equilibrium
Goods market
Loanable funds market
Factors of Production (FOP)
- FOP are inputs used to produce goods and services
- Two most important FOP’s are:
o Capital (K) – set of tools that workers use
o Labour (L) – the time people spend working
K = K̅
L = L̅
Overbar – the variable is fixed at some level
THE PRODUCTION FUNCTION
- Available production technology determines how much output is produced from given
amounts of capital and labour
- Economists express the relationship using a production function
- Letting Y denote the amount of output:
Y = F (K, L)
- The equation states that the output is a function of the amount of capital and labour
- Production function reflects the available technology for turning capital and labour into
output
- This, technology alters the production function
- Many production functions have a property called constant returns to scale
- The reason for this -> increase of equal percentage causes an increase in output in the same
percentage
- Mathematically, a production function has a constant returns to scale if for any positive
number z
𝓏K = F(𝓏K, 𝓏L)
- If capital and labour are multiplied by z, output is also multiplied by z
, THE SUPPLY OF GOODS AND SERVICES
- FOP and the production function together determine the quantity of goods and services
supplied
- Quantity of goods and services supplied = economy’s output
Y = F(K̅, L̅)
= Y̅
- The supply of capital and labour, and the technology are fixed, output is also fixed
FACTOR PRICES
- The distribution of national income is determined by factor price
- Factor prices are the amounts paid to each unit of the factors of production
- Two FOP’s:
o Capital -> rent paid to the owners of capital
o Labour-> wages paid for work done
- To understand factor prices and the distribution of income-> the demand for the factors of
production
DECISIONS FACING A COMPETITIVE FIRM Y = no. of units produced
- Simplest assumption to make about a typical firm is that it is K = no. of machines used
competitive
- Competitive firm-> small relative to the markets in which it L = no. of hours worked
trades, so it has little influence on market price
- To make its products, a firm needs two FOP’s -> capital and labour
- Holding constant the technology as expressed in the production function, the firm produces
more output only if it used more machines or if its employees work more hours
- Goal of a firm is to maximise profit
Profit = Revenue – Labour Costs – Capital Costs
= PY - WL – RK
- Costs include labour and capital costs
- To see how profit depends on product price
Profit = PF(K, L) – WL – RK
THE FIRM’S DEMAND OF FOP
MARGINAL PRODUCT OF LABOUR