Lecture 1 - Understanding the SDG’s - 7 februari
Corporate responsibility vs corporate sustainability
● Two (historically) distinctive concepts, now often used interchangeably
● Confusion led to the proliferation of constructs
○ Corporate social responsibility
○ Corporate social performance
○ Corporate citizenship
○ Triple bottom line
○ Shared value…
● “Corporate responsibility and sustainability tackle the relationship between business
and society.”
Evolution of the conceptualization of business-society relations
Corporate responsibility vs. corporate sustainability and convergence of the two concepts.
A focus on the history of corporate social responsibility
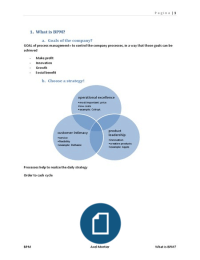
What is the purpose of a corporation (Lee, 2008)?
“My ambition is to employ still more men, to spread the benefits of this industrial system to
the greatest possible number, to help them build up their lives and their homes. To do this
we are putting the greatest share of our profits back in the business’ Ford
Lee (2008). A review of the theories or corporate social responsibility: Its evolutionary
path and the road ahead
- Rationalization of CSR: particular focus on tighter coupling with organizations’
financial goals
The Shareholder Primacy Norm
- “A business corporation is organized and carried on
primarily for the profit of the stockholders.” (Dodge v.
Ford Motor Co.)
- “The social responsibility of business is to increase its
profits” (M. Friedman, 1970)
What do managers and shareholders think today?
● Surveys in recent years show that CSR has become
important for managers
, ● The importance of considering the interest of non-shareholder stakeholders (such as
employees, local communities, the general public) is increasing to pursue in business
objectives.
What happened between 1917 (if not late 1970s) and late 1990s? Rationalization CSR
Focus more on mangerial and strategic issues > Source level of analysis
Two broad changes
○ Level of analysis: moved from the discussion of macro-social effects of CSR
to the organizational-level
○ Ethical orientation: the ethical and normative orientation has been made more
implicit than explicit, with a higher focus on performance
Evolution of the concept of CSR
Limitations of the business case for CSR concept
● Inconclusive empirical findings
● Even if a business case exist, the marginal value of social responsibility will
decrease as more corporations become socially responsible
● Little explanatory power to account for the recent organizational changes
○ Institutional factors (e.g. pressures from social movements)
○ Personal factors (e.g. personal ethics of managers)
● Business case driven CSR assumes that what is good for society should also be
good for corporations. But not necessarily true!
● Business case driven CSR will bias how corporations select their CSR strategy
,Strategic CS(R) implementation
”New wave in business is, forget corporate social responsibility and philanthropy – how do
you integrate this into your core business?” (Marc van Ameringen, in Prasso 2007)
- No consistent understanding of corporate sustainability & social responsibility
(CSSR)
- Many companies lack a strategic approach to CSSR and follow unsystematic
procedures
- Formal strategic planning could improve operational efficiency (Hahn, 2013)
> ISO 26000
Hahn (2013). ISO 26000 and the standardization of strategic management processes
for sustainability and corporate social responsibility
Existing guidelines
● ILO
● UN Global Compact Principles
● UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights
● ISO 26000 Guidance on Social Responsibility
● OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises
● SA 8000 certification
Research suggests ISO 26000 is the most significant instrument
A focus on two guidelines : The SDG Compass & The ISO 26000 standard
SDG Compass
- Launched in 2015 by GRI, the UN Global Compact and WBCSD
- “This tool shows companies how they can align their strategies, measure and
manage their contribution to reaching the SDG, and put sustainability at the heart of
their business strategy.”
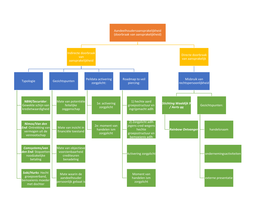
The SDG Compass presents five main steps that companies can
apply to maximize their contributions to the SDGs
Step 1: Understanding the SDGs
Step 2: Defining priorities
Step 3: Setting goals
, Step 4: Integrating
Step 5: Reporting and communicating
Focus of the SDG Compass
- Focus on large multinational enterprises
- Small and medium enterprises and other organizations are encouraged to use it as
a source of inspiration and adapt as necessary
ISO 26000
● Guidance on (corporate) social responsibility
● Launched by ISO in 2010
● “ISO 26000 [an international voluntary standard] provides guidance [rather than
requirements] on how businesses and organizations can operate in a socially
responsible way. This means acting in an ethical and transparent way that
contributes to the health and welfare of society [i.e. sustainable development].”
● Core concept: Social Responsibility
○ Responsibility of an organization for the impacts of its decisions and activities
on society and the environment, through transparent and ethical behaviour
that contributes to sustainable development
● Provides guidance for all types of organization,
regardless of their size or location
○ Not useful for strategy formulation
● Intended for both organizations beginning to
address social responsibility, and those more
experienced with its implementation
● Flexible and the user decides how to use it
● Builds on international norms and agreements
related to Social Responsibility
ISO 26000: key elements
ISO 26000: 7 principles of social responsibility
Corporate responsibility vs corporate sustainability
● Two (historically) distinctive concepts, now often used interchangeably
● Confusion led to the proliferation of constructs
○ Corporate social responsibility
○ Corporate social performance
○ Corporate citizenship
○ Triple bottom line
○ Shared value…
● “Corporate responsibility and sustainability tackle the relationship between business
and society.”
Evolution of the conceptualization of business-society relations
Corporate responsibility vs. corporate sustainability and convergence of the two concepts.
A focus on the history of corporate social responsibility
What is the purpose of a corporation (Lee, 2008)?
“My ambition is to employ still more men, to spread the benefits of this industrial system to
the greatest possible number, to help them build up their lives and their homes. To do this
we are putting the greatest share of our profits back in the business’ Ford
Lee (2008). A review of the theories or corporate social responsibility: Its evolutionary
path and the road ahead
- Rationalization of CSR: particular focus on tighter coupling with organizations’
financial goals
The Shareholder Primacy Norm
- “A business corporation is organized and carried on
primarily for the profit of the stockholders.” (Dodge v.
Ford Motor Co.)
- “The social responsibility of business is to increase its
profits” (M. Friedman, 1970)
What do managers and shareholders think today?
● Surveys in recent years show that CSR has become
important for managers
, ● The importance of considering the interest of non-shareholder stakeholders (such as
employees, local communities, the general public) is increasing to pursue in business
objectives.
What happened between 1917 (if not late 1970s) and late 1990s? Rationalization CSR
Focus more on mangerial and strategic issues > Source level of analysis
Two broad changes
○ Level of analysis: moved from the discussion of macro-social effects of CSR
to the organizational-level
○ Ethical orientation: the ethical and normative orientation has been made more
implicit than explicit, with a higher focus on performance
Evolution of the concept of CSR
Limitations of the business case for CSR concept
● Inconclusive empirical findings
● Even if a business case exist, the marginal value of social responsibility will
decrease as more corporations become socially responsible
● Little explanatory power to account for the recent organizational changes
○ Institutional factors (e.g. pressures from social movements)
○ Personal factors (e.g. personal ethics of managers)
● Business case driven CSR assumes that what is good for society should also be
good for corporations. But not necessarily true!
● Business case driven CSR will bias how corporations select their CSR strategy
,Strategic CS(R) implementation
”New wave in business is, forget corporate social responsibility and philanthropy – how do
you integrate this into your core business?” (Marc van Ameringen, in Prasso 2007)
- No consistent understanding of corporate sustainability & social responsibility
(CSSR)
- Many companies lack a strategic approach to CSSR and follow unsystematic
procedures
- Formal strategic planning could improve operational efficiency (Hahn, 2013)
> ISO 26000
Hahn (2013). ISO 26000 and the standardization of strategic management processes
for sustainability and corporate social responsibility
Existing guidelines
● ILO
● UN Global Compact Principles
● UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights
● ISO 26000 Guidance on Social Responsibility
● OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises
● SA 8000 certification
Research suggests ISO 26000 is the most significant instrument
A focus on two guidelines : The SDG Compass & The ISO 26000 standard
SDG Compass
- Launched in 2015 by GRI, the UN Global Compact and WBCSD
- “This tool shows companies how they can align their strategies, measure and
manage their contribution to reaching the SDG, and put sustainability at the heart of
their business strategy.”
The SDG Compass presents five main steps that companies can
apply to maximize their contributions to the SDGs
Step 1: Understanding the SDGs
Step 2: Defining priorities
Step 3: Setting goals
, Step 4: Integrating
Step 5: Reporting and communicating
Focus of the SDG Compass
- Focus on large multinational enterprises
- Small and medium enterprises and other organizations are encouraged to use it as
a source of inspiration and adapt as necessary
ISO 26000
● Guidance on (corporate) social responsibility
● Launched by ISO in 2010
● “ISO 26000 [an international voluntary standard] provides guidance [rather than
requirements] on how businesses and organizations can operate in a socially
responsible way. This means acting in an ethical and transparent way that
contributes to the health and welfare of society [i.e. sustainable development].”
● Core concept: Social Responsibility
○ Responsibility of an organization for the impacts of its decisions and activities
on society and the environment, through transparent and ethical behaviour
that contributes to sustainable development
● Provides guidance for all types of organization,
regardless of their size or location
○ Not useful for strategy formulation
● Intended for both organizations beginning to
address social responsibility, and those more
experienced with its implementation
● Flexible and the user decides how to use it
● Builds on international norms and agreements
related to Social Responsibility
ISO 26000: key elements
ISO 26000: 7 principles of social responsibility