Calcium functions:
1. Structural: bone, teeth
2. Neuromuscular: release for neurotransmitters, initiation of muscle
contractions
3. Enzymic function: coenzyme for coagulation factors (transfusion
science)
4. Hormonal: intracellular second messenger
5. Cell adhesion
Plasma calcium exists in 3 forms:
1. Free ionised (Ca2+): 47% physiologically active
2. protein-bound : 46%
3. Complexed calcium (citrates, phosphates): 7%
Reference range:
- Total calcium 2.20-2.60 mmol/L
- Ionised calcium 1.20-1.37 mmol/L
- If the albumin concentration in the blood
changes, so will the total calcium concentration,
but not the free ionized Ca2+
Changes in [albumin] affect total calcium but not
[Ca2+]: correction factor is applied to get correct
[calcium]
1. If [albumin] < 40g/L:
a. Correct [calcium] = measured total
[calcium] + 0.02 (40 - [albumin])
2. If [albumin] > 45g/L:
a. Correct [calcium] = measured total
[calcium] - 0.02 ([albumin] - 45)
3. Alternative: measure ionised plasma [Ca2+]
directly
Factors affecting plasma [Ca2+] - pH
- Acid-base balance
- Binding of calcium to protein is pH dependent
Acidosis: high plasma [Ca2+]
Alkalosis: low plasma [Ca2+]
(Doesn’t change TOTAL calcium)
Regulation of plasma calcium
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- Calcitriol or also called 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol or 1,25-DHCC
, Vitamin D derivative:
1. Diet: Cholecalciferol
2. Skin: Cholecalciferol
3. Liver: 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
4. Kidneys: 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol; 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (inactive)
1,25-DHCC synthesis activated by:
1. Increase in PTH
2. Decrease in Calcium
3. Decrease in Phosphate
Synthesis of calcitriol: Normal/high plasma calcium 24-hydroxylase converts 25-HCC to 24,25-DHCC (inactive)
Calcitriol function:
- Increase calcium absorption in gut
- Increase phosphate absorption in gut
- Increase bone resorption
Calcitonin - opposes PTH function:
1. Synthesised in C cells of thyroid
a. 32 amino acid peptide
b. Released in response to increase of Ca2+, inhibited by decrease of Ca2+
2. Inhibits Ca2+ release from bone
3. Inhibits renal calcium reabsorption
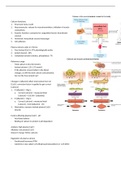
Regulation of calcium homeostasis
1. Structural: bone, teeth
2. Neuromuscular: release for neurotransmitters, initiation of muscle
contractions
3. Enzymic function: coenzyme for coagulation factors (transfusion
science)
4. Hormonal: intracellular second messenger
5. Cell adhesion
Plasma calcium exists in 3 forms:
1. Free ionised (Ca2+): 47% physiologically active
2. protein-bound : 46%
3. Complexed calcium (citrates, phosphates): 7%
Reference range:
- Total calcium 2.20-2.60 mmol/L
- Ionised calcium 1.20-1.37 mmol/L
- If the albumin concentration in the blood
changes, so will the total calcium concentration,
but not the free ionized Ca2+
Changes in [albumin] affect total calcium but not
[Ca2+]: correction factor is applied to get correct
[calcium]
1. If [albumin] < 40g/L:
a. Correct [calcium] = measured total
[calcium] + 0.02 (40 - [albumin])
2. If [albumin] > 45g/L:
a. Correct [calcium] = measured total
[calcium] - 0.02 ([albumin] - 45)
3. Alternative: measure ionised plasma [Ca2+]
directly
Factors affecting plasma [Ca2+] - pH
- Acid-base balance
- Binding of calcium to protein is pH dependent
Acidosis: high plasma [Ca2+]
Alkalosis: low plasma [Ca2+]
(Doesn’t change TOTAL calcium)
Regulation of plasma calcium
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- Calcitriol or also called 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol or 1,25-DHCC
, Vitamin D derivative:
1. Diet: Cholecalciferol
2. Skin: Cholecalciferol
3. Liver: 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
4. Kidneys: 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol; 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (inactive)
1,25-DHCC synthesis activated by:
1. Increase in PTH
2. Decrease in Calcium
3. Decrease in Phosphate
Synthesis of calcitriol: Normal/high plasma calcium 24-hydroxylase converts 25-HCC to 24,25-DHCC (inactive)
Calcitriol function:
- Increase calcium absorption in gut
- Increase phosphate absorption in gut
- Increase bone resorption
Calcitonin - opposes PTH function:
1. Synthesised in C cells of thyroid
a. 32 amino acid peptide
b. Released in response to increase of Ca2+, inhibited by decrease of Ca2+
2. Inhibits Ca2+ release from bone
3. Inhibits renal calcium reabsorption
Regulation of calcium homeostasis