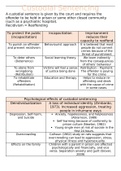
Custodial Sentencing
A custodial sentence is given by the court and requires the
offender to be held in prison or some other closed community
(such as a psychiatric hospital).
Recidivism = Reoffending
To protect the public Incapacitation Imprisonment
(incapacitation) reduces their
capacity to reoffend
To punish an offender Behaviourist approach It is believed that most
and prevent recidivism people do not commit
crimes because of the
threat of punishment
To deter others Social learning theory We learn indirectly
(Deterrence) from the consequences
of others’ behaviour
To atone from Victims will feel a sense Retribution – Payment.
wrongdoing of justice being done The offender is paying
(Retribution) for the crime
To rehabilitate Education and therapy Helps to reduce re-
offenders offending and deals
(Rehabilitation) with the cause of crime
in some cases.
Psychological effects of custodial sentencing
Deindividualization A loss of individual identity (Zimbardo,
1973). Increased aggression, treating
people in inhumane ways
Depression, Self-harm, Anxiety, hopelessness, and helplessness
and Suicide (Abramson, 1989)
Self-harming because of conformity to
prison culture (Newton, 1982)
Young single men at risk of suicide in the
first 24 hours.
Overcrowding Calhoun (1962) study on rats suggests that
overcrowding can lead to aggression, stress,
physical illness and hypersexuality.
Effects on the family Children with a parent in prison are affected
psychologically and financially, and vice
versa. Separation anxiety and guilt (Glover,
2009)
A custodial sentence is given by the court and requires the
offender to be held in prison or some other closed community
(such as a psychiatric hospital).
Recidivism = Reoffending
To protect the public Incapacitation Imprisonment
(incapacitation) reduces their
capacity to reoffend
To punish an offender Behaviourist approach It is believed that most
and prevent recidivism people do not commit
crimes because of the
threat of punishment
To deter others Social learning theory We learn indirectly
(Deterrence) from the consequences
of others’ behaviour
To atone from Victims will feel a sense Retribution – Payment.
wrongdoing of justice being done The offender is paying
(Retribution) for the crime
To rehabilitate Education and therapy Helps to reduce re-
offenders offending and deals
(Rehabilitation) with the cause of crime
in some cases.
Psychological effects of custodial sentencing
Deindividualization A loss of individual identity (Zimbardo,
1973). Increased aggression, treating
people in inhumane ways
Depression, Self-harm, Anxiety, hopelessness, and helplessness
and Suicide (Abramson, 1989)
Self-harming because of conformity to
prison culture (Newton, 1982)
Young single men at risk of suicide in the
first 24 hours.
Overcrowding Calhoun (1962) study on rats suggests that
overcrowding can lead to aggression, stress,
physical illness and hypersexuality.
Effects on the family Children with a parent in prison are affected
psychologically and financially, and vice
versa. Separation anxiety and guilt (Glover,
2009)