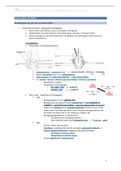
The Vagus Nerve (CN X)
Is a diverse nerve that offers many different modalities of innervation
Due to its widespread function, pathology of the vagus nerve can manifest
The vagus nerve is associated with structures derived from the forth
pharyngeal arch
Its actions include:
Sensory – acts to innervate the skin around the external auditory meatus, the
internal laryngopharynx and larynx, and provides visceral sensation to the
heart and other abdominal viscera
Special sensory – provides taste sensation to the root of the tongue and
epiglottis
Motor – supplies most of the muscles of the pharynx, soft palate and larynx
Parasympathetic – supplies all smooth muscle in the trachea, bronchi and
gastrointestinal tract and also regulates heart rhythm
Anatomical course:
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve, extending from the head to the
lower abdomen
In the head –
The vagus nerve arises from the medulla oblongata of the brainstem, in
between the pyramid and the inferior cerebellar peduncle
It leaves the cranium via the jugular foramen, with the glossopharyngeal
nerve and accessory nerve (CN IX and CN XI)
While still in the cranium, the auricular branch splits from the vagus nerve,
which acts to supply sensation to the external auditory meatus and external
ear canal
In the neck –
Here the vagus nerve enters the carotid
sheath, passing inferiorly with the
internal jugular vein and common
carotid artery
At the base of the neck the vagus
nerve splits into:
1. Right vagus nerve – passes
anterior to the subclavian artery
and posterior to the
sternoclavicular joint, and enters
the thorax
2. Left vagus nerve – passes
inferiorly between the left
common carotid and left
Is a diverse nerve that offers many different modalities of innervation
Due to its widespread function, pathology of the vagus nerve can manifest
The vagus nerve is associated with structures derived from the forth
pharyngeal arch
Its actions include:
Sensory – acts to innervate the skin around the external auditory meatus, the
internal laryngopharynx and larynx, and provides visceral sensation to the
heart and other abdominal viscera
Special sensory – provides taste sensation to the root of the tongue and
epiglottis
Motor – supplies most of the muscles of the pharynx, soft palate and larynx
Parasympathetic – supplies all smooth muscle in the trachea, bronchi and
gastrointestinal tract and also regulates heart rhythm
Anatomical course:
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve, extending from the head to the
lower abdomen
In the head –
The vagus nerve arises from the medulla oblongata of the brainstem, in
between the pyramid and the inferior cerebellar peduncle
It leaves the cranium via the jugular foramen, with the glossopharyngeal
nerve and accessory nerve (CN IX and CN XI)
While still in the cranium, the auricular branch splits from the vagus nerve,
which acts to supply sensation to the external auditory meatus and external
ear canal
In the neck –
Here the vagus nerve enters the carotid
sheath, passing inferiorly with the
internal jugular vein and common
carotid artery
At the base of the neck the vagus
nerve splits into:
1. Right vagus nerve – passes
anterior to the subclavian artery
and posterior to the
sternoclavicular joint, and enters
the thorax
2. Left vagus nerve – passes
inferiorly between the left
common carotid and left