Overview of protozoan parasites
• Possess eukaryotic organelles
• Exhibit typical features of eukaryotic cells
• Many have unique organelles as well
• Life stages
o Trophozoite – active, vegetative, feeding, most are motile
o Cyst
▪ Dormant, in unfavourable environments
▪ Metabolically inactive, don’t replicate
▪ Can last days, weeks, months
• Classified by motility and life cycle
o Amoeba – move by pseudopods
o Flagellates – move by flagella
o Ciliates – move by cilia
o Sporoza (apicomplexan) – complex life cycle, non-motile
• In the Kingdom Protista but not all are genetically similar – hence why classified by motility instead
of genetics
Life cycle
• Encystation – trophozoites → cysts
• Excystation – cysts → trophozoites
• Thick cell wall protects cysts against desiccation, lack of nutrients, heat and antimicrobials
• Number of cues needed for excystation to occur
• Direct life cycle examples
o Balantidium coli (ciliate)
o Giardia intestinalis (flagellate)
o Naegleria fowleri (amoeba)
• Indirect lifecycle
o Sexual reproduction occurs in definitive host – introduces genetic diversity
o Intermediate host usually human
o Plasmodium spp (sporozoan)
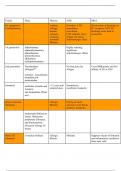
• Protozoan disease
o Sporozoan – infected and killed more than anything else in history
, ▪ Malaria
▪ Toxoplasmosis
▪ Cryptosporidiosis
o Amoeba
▪ Amebiasis
▪ Primary amoebic meningoenchaphalitis
o Ciliates – balantidiasis
o Flagellates
▪ Giardiasis
▪ Sleeping sickness
▪ Chagas disease
▪ Leishmaniasis
o Intestinal – diarrhoea
o Blood
o Tissue – blood, organ, brain
o Vast majority in developing countries – ‘neglected disease’
Infection route
• Contact/penetration of eye – Acanthamoeba
• Vector-borne – Plasmodium (malaria)
• Inhalation – Naegleria
• Faecal-oral, ingestion – Balantidium, Giardia
• Contact/penetration of skin – Schistosoma
• Sexual contact – Trichomonas
Plasmodium spp
• Sporozoa/Apicomplexa
o Group of obligate parasites
o Transmitted by Anopholes mosquitoes
o 40% of world’s population live in endemic areas
o Highest number of deaths
o Toxoplasma gondii (toxoplasmosis)
▪ 1 in 3 of world’s population infected (most prevalent)
▪ Mild symptoms unless weakened immunity
▪ Behavioural changes in host
▪ Definitive host is cats – hence why it is most prevalent
o Cryptosporidium spp (Cryptosporidiosis)
▪ Not as common (4000 cases/year in UK)
▪ Intestinal parasites
▪ Farmed animals are a reservoir
• Apicoplast
o Organelle for specific fatty acid metabolism
o Tetracycline disrupts Apicoplast function but doesn’t kill cell
o Not well understood
• Phylogenetic clade
o Group of organisms on one branch of phylogeny tree
o Apicomplexa clade grouped as all have Apicoplast and are genetically similar
• 5 known human Plasmodium species that cause malaria
o P. falciparium – strongest pathogenicity
o P. vivax – most common (less complications)
o P. ovale
o P. malariae