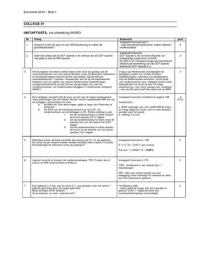
Questions: Thermal Physics
1) absolute zero is the minimum
Internal Energy (U) FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS energy of an object (-273-c)
= to the sum of the kinetic and potential energy of a system AU = Q -W work done 2) Internal energy is the sum of k
depends on: temperature, pressure and volume change in ↗ ↑ heat potential energy of a system.
Q and W
Ideal Gas - only has KE as particles do not interact internal energy transfer are forms of 3) If internal energy of an ideal
energy
so internal energy = sum of KE of the particles. only then the equation is U
KE of one mole = ⅔ RT - → U decreases, loses heat to surroundings 4) Heat is the flow of energy from
+ Q → U increases, gains heat cold due to a difference in temp
Total KE = number of moles of particles (n) ✗ ERT - W → work of object → compresses: inc U 5) Thermal Equilibrium occurs whe
↳ We know sum of KE = Internal energy + W → work by object → expands : dec U temperatures of both objects ar
so U=¾nRT Energy is conserved. 6) To increase the thermal energ
system we can increase the hea
Internal energy of ideal gas α Temperature HEAT TRANSFER by increasing the work done on
smallest temperature possible → absolute zero heat only transfers from: hot → cold 7) During a change of state potent
[273.15-Cor 0K] heat transfer is faster when the difference in of particles change but KE
smallest internal energy temperature between objects is larger. basically how 8) To determine the energy require
÷ An object with temperature of absolute zero has Two objects with same temperatures much energy is the temperature of a substance
minimum internal energy. = THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM needed to heat up. 9) W=pΔV
In a real gas internal energy also depends on temperature P 2 at constant pressur
and volume as PE occurs. DQ - MCAT Specific heat capacity: W = PX AV = area
ENERG Y TRANSFER AS WORK m= mass • the amount of energy
W = FAX → W = PAY C = specific heat capacity needed to raise the temp V
if gas is compressed DV = (-) AT = change in temperature of 1 KG of the substance 10) First law of thermodynamics
if gas expands AV = (t) ΔQ= change in heat by 1K. (JKG-'K-') AU = change in internal ene
p For constant pressure only, we can use W =p DV Q = heat transfer
2 • constant pressure W = work done by system
..
ΔW
work done is the area SOLIDS LIQUIDS 11) specific heat capacity is the
underneath graph! Good conductors of heat • most do not contain free electrons "raise the temperature of T
AV V • metals : sea of free electrons so are not good conductors of heat. substance by 1K
p
• pressure is changing → small specific heat capacities as • particles are free to move around 12) specific latent heat of a subst
cannot use ΔW=pΔV applying a little heat to a metal will cause so specific heat capacities are larger. required to change the state of
AW a large increase in temperature. E. g water:c-4200J KG"K" substance whilst temperature
V Bad conductors of heat metal iron: C-450 JKG" K" 13) U -¾ NRT Internal energy
Generally, no work is done on • insulators : no free electrons is equal to the KE o
solids or liquids, only gases! as volume → large heat capacities gas assumes there are no in
is constant for solids and liquids. Their internal energy is due to and so there is no potential
So 1st law of thermodynamics for solids and liquids: vibrations of atoms. 14) Boyles law - Temperature i
ΔU=ΔQ ΔW=O pressure is inversely proportio
1) absolute zero is the minimum
Internal Energy (U) FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS energy of an object (-273-c)
= to the sum of the kinetic and potential energy of a system AU = Q -W work done 2) Internal energy is the sum of k
depends on: temperature, pressure and volume change in ↗ ↑ heat potential energy of a system.
Q and W
Ideal Gas - only has KE as particles do not interact internal energy transfer are forms of 3) If internal energy of an ideal
energy
so internal energy = sum of KE of the particles. only then the equation is U
KE of one mole = ⅔ RT - → U decreases, loses heat to surroundings 4) Heat is the flow of energy from
+ Q → U increases, gains heat cold due to a difference in temp
Total KE = number of moles of particles (n) ✗ ERT - W → work of object → compresses: inc U 5) Thermal Equilibrium occurs whe
↳ We know sum of KE = Internal energy + W → work by object → expands : dec U temperatures of both objects ar
so U=¾nRT Energy is conserved. 6) To increase the thermal energ
system we can increase the hea
Internal energy of ideal gas α Temperature HEAT TRANSFER by increasing the work done on
smallest temperature possible → absolute zero heat only transfers from: hot → cold 7) During a change of state potent
[273.15-Cor 0K] heat transfer is faster when the difference in of particles change but KE
smallest internal energy temperature between objects is larger. basically how 8) To determine the energy require
÷ An object with temperature of absolute zero has Two objects with same temperatures much energy is the temperature of a substance
minimum internal energy. = THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM needed to heat up. 9) W=pΔV
In a real gas internal energy also depends on temperature P 2 at constant pressur
and volume as PE occurs. DQ - MCAT Specific heat capacity: W = PX AV = area
ENERG Y TRANSFER AS WORK m= mass • the amount of energy
W = FAX → W = PAY C = specific heat capacity needed to raise the temp V
if gas is compressed DV = (-) AT = change in temperature of 1 KG of the substance 10) First law of thermodynamics
if gas expands AV = (t) ΔQ= change in heat by 1K. (JKG-'K-') AU = change in internal ene
p For constant pressure only, we can use W =p DV Q = heat transfer
2 • constant pressure W = work done by system
..
ΔW
work done is the area SOLIDS LIQUIDS 11) specific heat capacity is the
underneath graph! Good conductors of heat • most do not contain free electrons "raise the temperature of T
AV V • metals : sea of free electrons so are not good conductors of heat. substance by 1K
p
• pressure is changing → small specific heat capacities as • particles are free to move around 12) specific latent heat of a subst
cannot use ΔW=pΔV applying a little heat to a metal will cause so specific heat capacities are larger. required to change the state of
AW a large increase in temperature. E. g water:c-4200J KG"K" substance whilst temperature
V Bad conductors of heat metal iron: C-450 JKG" K" 13) U -¾ NRT Internal energy
Generally, no work is done on • insulators : no free electrons is equal to the KE o
solids or liquids, only gases! as volume → large heat capacities gas assumes there are no in
is constant for solids and liquids. Their internal energy is due to and so there is no potential
So 1st law of thermodynamics for solids and liquids: vibrations of atoms. 14) Boyles law - Temperature i
ΔU=ΔQ ΔW=O pressure is inversely proportio