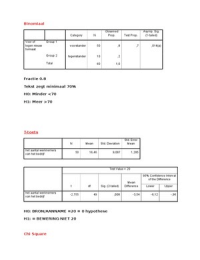
ABNORMAL | GLOSSARY
CBT: Cognitive behavioural therapy - aka, cognitive restructuring. This is based on
Beck's theory of faulty thinking. The job of the therapist is to help reshape the
schema of the client by pointing out errors in thinking as well as giving "homework"
which helps them to challenge how they think.
mCBT: A type of CBT that aims to help clients let go of negative thinking patterns
instead of being obsessed with them.
Comorbidity: The idea that often there is more than one disorder that influences a
person's behaviour. This is part of why diagnosis is difficult.
Cross-cultural psychotherapy: Also known as "intercultural counselling" or
"multicultural therapy." This is when the therapist is from a different culture from the
patient. The therapist adapts therapeutic methods that have been shown to be
effective to meet the cultural needs of the patient.
Diathesis-Stress Model: The theory that behavior may be the result of a genetic
predisposition which is "activated" by stress from life experiences. This approach is
an interactionist approach which looks at how biological and environmental factors
interact in order to cause behavior - in this case, depression.
Discontinuation syndrome: Withdrawal symptoms from taking medication.
Etiology: The origin or potential cause of a disorder.
Genetic vulnerability: The theory that some people may have the right genes for a
disorder, but that they may not have been "turned on." These people have a
potential to develop the disorder depending on life circumstances, diet or level of
exercise. Other factors may also play a role in whether the genes are expressed or
not.
Iatrogenic effects: Symptoms that result in response to a treatment, which then can
be mistaken as part of the disorder. The classic example is tardive dyskinesia,
involuntary, repetitive body movements which were the result of taking
chlorpromazine to treat schizophrenia. Another example comes from Freudian
therapy where false memories may have been created as part of trying to retrieve
repressed memories or dream analysis. This could have led to anxiety which would
further complicate the diagnosis and treatment.
Indigenous psychotherapy: These therapies are embedded within a culture and do
not include anyone from outside the culture. They are carried out by someone who is
sanctioned within the community to be a therapist. Indigenous healing encompasses
therapeutic beliefs and practices that are rooted within a given culture - for example,
heavy reliance on family and community networks, as well as spiritual and religious
beliefs. These practices are difficult to transfer to a different cultural setting.
Reactivity: When individuals alter their performance or behavior due to the
awareness that they are being observed. This is one of the fundamental problems of
diagnosis.
, Relapse rate: The rate at which symptoms return after treatment has been
discontinued.
Reporting bias: Selective revealing or suppression of information by clients when
meeting with a doctor - for example, about past medical history, smoking, sexual
experiences. Reporting bias also refers to the extent to which different genders and
ethnic groups seek psychological help and the types of information that they are
willing to disclose to a psychiatrist.
Rumination: Repetitively focusing on one's symptoms of depression and the
possible causes and consequences of these symptoms.
SSRIs: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors - the most famous of which is
Prozac. SSRIs block the reuptake of serotonin by the terminal buttons, leaving more
in the synapse.
ABNORMAL | THEORIES + STUDIES
BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT
(LEUCHTER ET AL + ELKIN ET AL)
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors are antidepressant drugs that are routinely
used to treat depression. SSRIs work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin back into
the presynaptic neuron, this leads to more serotonin in the synapse. Their use is
based on the serotonin hypothesis.
Evaluation
→ SSRIs are better than placebos
→ They are cheap and easy to prescribe
→ Faster improvement than in therapy
→ SSRIs cause side effects
→ Higher rate of relapse
→ Alleviate symptoms but don't find cause
Leucher et al
A: To see changes in brain function of depressed subjects during treatment with
placebo
M: Brain function was examined in 51 patients with depression. Patients received a
placebo or active antidepressant medication. EEG was used to compare brain
function. 2 different SSRIs (Selective serotonin EE-uptake inhibitor) were randomly
allocated to participants. Lasted 9 weeks.
R: A significant increase in activity in the prefrontal cortex with placebo group.
Patients in both groups got better (placebo was just as effective)
Elkin et al
A: To compare the effectiveness of treatments for depression
M: The study involved 280 depressed people, treated by 28 clinicians. Participants
were randomly assigned to one of the following treatment groups: an antidepressant
CBT: Cognitive behavioural therapy - aka, cognitive restructuring. This is based on
Beck's theory of faulty thinking. The job of the therapist is to help reshape the
schema of the client by pointing out errors in thinking as well as giving "homework"
which helps them to challenge how they think.
mCBT: A type of CBT that aims to help clients let go of negative thinking patterns
instead of being obsessed with them.
Comorbidity: The idea that often there is more than one disorder that influences a
person's behaviour. This is part of why diagnosis is difficult.
Cross-cultural psychotherapy: Also known as "intercultural counselling" or
"multicultural therapy." This is when the therapist is from a different culture from the
patient. The therapist adapts therapeutic methods that have been shown to be
effective to meet the cultural needs of the patient.
Diathesis-Stress Model: The theory that behavior may be the result of a genetic
predisposition which is "activated" by stress from life experiences. This approach is
an interactionist approach which looks at how biological and environmental factors
interact in order to cause behavior - in this case, depression.
Discontinuation syndrome: Withdrawal symptoms from taking medication.
Etiology: The origin or potential cause of a disorder.
Genetic vulnerability: The theory that some people may have the right genes for a
disorder, but that they may not have been "turned on." These people have a
potential to develop the disorder depending on life circumstances, diet or level of
exercise. Other factors may also play a role in whether the genes are expressed or
not.
Iatrogenic effects: Symptoms that result in response to a treatment, which then can
be mistaken as part of the disorder. The classic example is tardive dyskinesia,
involuntary, repetitive body movements which were the result of taking
chlorpromazine to treat schizophrenia. Another example comes from Freudian
therapy where false memories may have been created as part of trying to retrieve
repressed memories or dream analysis. This could have led to anxiety which would
further complicate the diagnosis and treatment.
Indigenous psychotherapy: These therapies are embedded within a culture and do
not include anyone from outside the culture. They are carried out by someone who is
sanctioned within the community to be a therapist. Indigenous healing encompasses
therapeutic beliefs and practices that are rooted within a given culture - for example,
heavy reliance on family and community networks, as well as spiritual and religious
beliefs. These practices are difficult to transfer to a different cultural setting.
Reactivity: When individuals alter their performance or behavior due to the
awareness that they are being observed. This is one of the fundamental problems of
diagnosis.
, Relapse rate: The rate at which symptoms return after treatment has been
discontinued.
Reporting bias: Selective revealing or suppression of information by clients when
meeting with a doctor - for example, about past medical history, smoking, sexual
experiences. Reporting bias also refers to the extent to which different genders and
ethnic groups seek psychological help and the types of information that they are
willing to disclose to a psychiatrist.
Rumination: Repetitively focusing on one's symptoms of depression and the
possible causes and consequences of these symptoms.
SSRIs: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors - the most famous of which is
Prozac. SSRIs block the reuptake of serotonin by the terminal buttons, leaving more
in the synapse.
ABNORMAL | THEORIES + STUDIES
BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT
(LEUCHTER ET AL + ELKIN ET AL)
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors are antidepressant drugs that are routinely
used to treat depression. SSRIs work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin back into
the presynaptic neuron, this leads to more serotonin in the synapse. Their use is
based on the serotonin hypothesis.
Evaluation
→ SSRIs are better than placebos
→ They are cheap and easy to prescribe
→ Faster improvement than in therapy
→ SSRIs cause side effects
→ Higher rate of relapse
→ Alleviate symptoms but don't find cause
Leucher et al
A: To see changes in brain function of depressed subjects during treatment with
placebo
M: Brain function was examined in 51 patients with depression. Patients received a
placebo or active antidepressant medication. EEG was used to compare brain
function. 2 different SSRIs (Selective serotonin EE-uptake inhibitor) were randomly
allocated to participants. Lasted 9 weeks.
R: A significant increase in activity in the prefrontal cortex with placebo group.
Patients in both groups got better (placebo was just as effective)
Elkin et al
A: To compare the effectiveness of treatments for depression
M: The study involved 280 depressed people, treated by 28 clinicians. Participants
were randomly assigned to one of the following treatment groups: an antidepressant