Alkene reactions - Study guides, Class notes & Summaries
Looking for the best study guides, study notes and summaries about Alkene reactions? On this page you'll find 331 study documents about Alkene reactions.
Page 4 out of 331 results
Sort by

-
BCH 462 Exam 4 Questions With 100% Correct Answers
- Exam (elaborations) • 20 pages • 2024
-
- $13.49
- + learn more
BCH 462 Exam 4 Questions With 100% Correct Answers Fatty Acid Synthesis - answerFatty acids are built in several passes, processing one acetate unit at a time. The acetate is coming from activated malonate in the form of malonyl-CoA. Each pass involves reduction of a carbonyl carbon to a methylene carbon. Overall, repeating four-step sequence that elongates the fatty acyl chain by two carbons at each step, uses NADPH as the electron donor. Two enzyme-bound -SH groups serve as activating...

-
GCSE AQA Chemistry Paper 2 - C10 Questions & Correct Answers/ Graded A+
- Exam (elaborations) • 5 pages • 2024
- Available in package deal
-
- $10.09
- + learn more
What is an organic compund? : The substances that form the basis of all living things; all contain carbon atoms What is a functional group? : An atom or a group of atoms which give organic compounds their characteristics What is a homologous series? : A group of organic compounds that react in a similar way (same functional group) Describe the combustion of alkenes : Produces CO₂ and H₂0 Smoky, yellow flame e.g. ethene + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water 2 C₂H₄ + 3O₂ -&g...

-
Chem 210 – Reactions Questions 100% Answered!
- Exam (elaborations) • 6 pages • 2024
- Available in package deal
-
- $13.99
- + learn more
Reagent = Nucleophile Only - ANSWER1° = Sn2 2° = Sn2 3° = Sn1 + E1 (polar medium necessary) Reagent = Strong Nucleophile & Strong Base - ANSWER1° = Sn2 2° = E2 3° = E2 Reagent = Weak Nucleophile and Weak Base - ANSWER1°/2° = No Reaction 3°/resonance stabilized carbocation = Sn1 + E1 (polar medium necessry Reagent = Base Only - ANSWER1° = E2 or Sn2 (if unhindered and no beta-hydrogen with unhindered base) 2° = E2 3° = E2 Examples of Only Nucleophiles - ANSWERCl⁻, ...

-
Organic Chemistry Exam 4 Questions and Answers
- Exam (elaborations) • 5 pages • 2024
- Available in package deal
-
- $10.49
- + learn more
acetylenes = - Answer-alkynes olefins = - Answer-alkenes E = - Answer-trans Z = - Answer-cis stability of cis vs. trans - Answer-trans is more stable hydrogenation - Answer-exothermic addition of H to an alkene relate the heats of reaction for trans-butene, cis-butene, and 1-butene. - Answer-1-butene > cis-2-butene > trans-2-butene (most stable) stabilities of alkenes (substitution) - Answer-tetra- > tri- > di-> mono- > un- stabilities of alkenes (status...

-
CHEM 210 Final Exam Study Guide Exam 1 Final Review Questions with Answers
- Exam (elaborations) • 18 pages • 2023
- Available in package deal
-
- $10.99
- + learn more
What are the differences between aliphatic (including alkanes, alkenes,alkynes and cyclic compounds) aromatic hydrocarbons are. - ALIPHATIC Hydrocarbon: Non-aromatic -Alkanes & CycloAlkanes:single bonds; saturated:Contain only carbon and hydrogen & C-C & C-H single bonds -Alkenes:double bond(s) -Alkynes: triple bond(s) *alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated: at least one C-C double or triple bond(s) AROMATIC Hydrocarbon: benzene ring What is the trend in solubility and boiling point/mel...

-
Organic Chemistry McMurry CH 17 Practice Exam Questions And Answers Guaranteed Pass.
- Exam (elaborations) • 6 pages • 2024
- Available in package deal
-
- $12.99
- + learn more
Primary Alcohol - correct answer the -OH of alcohol is attached to an end carbon Secondary Alcohol - correct answer An alcohol in which the -OH group is attached to a carbon atom that is attached to two carbon chains and one hydrogen atom. Tertiary Alcohol - correct answer An alcohol in which the -OH group is attached to a carbon atom that is attached to three carbon atoms and no ...

-
Chem 219 Unit 5 Exam Questions With 100% Correct Answers
- Exam (elaborations) • 10 pages • 2024
- Available in package deal
-
- $12.49
- + learn more
Chem 219 Unit 5 Exam Questions With 100% Correct Answers Generic formula for alcohols - answerR-OH phenol - answerhydroxy-substituted aromatic molecules (any compound with an -OH attached to a benzene ring) IUPAC system rules for naming organic alcohols - answer- organic alcohols are named by replacing the suffix of the parent chain of the molecule with the suffix -ol - The parent chain is numbered so as to give the hydroxyl group the lowest possible number. (examples: 1-propanol, and cy...
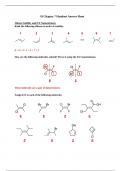
-
CHM 2210 SI Chapter 7 Handout Answer Sheet
- Other • 11 pages • 2023
-
- $17.49
- + learn more
SI Chapter 7 Handout Answer Sheet Alkene Stability and E/Z Nomenclature Rank the following alkenes in order of stability. 6 > 4 > 3 > 1 > 2 > 7 > 5 How are the following molecules related? Prove it using the E/Z nomenclature. These molecules are a pair of diastereomers. Assign E/Z to each of the following molecules. Assign E/Z to the following molecules. Name each of the following molecules using IUPAC nomenclature. Elimination Reactions Complete the general reaction ...

-
BCH 462 Exam 4 Questions With 100% Correct Answers
- Exam (elaborations) • 20 pages • 2024
-
- $13.49
- + learn more
BCH 462 Exam 4 Questions With 100% Correct Answers Fatty Acid Synthesis - answerFatty acids are built in several passes, processing one acetate unit at a time. The acetate is coming from activated malonate in the form of malonyl-CoA. Each pass involves reduction of a carbonyl carbon to a methylene carbon. Overall, repeating four-step sequence that elongates the fatty acyl chain by two carbons at each step, uses NADPH as the electron donor. Two enzyme-bound -SH groups serve as activating...

-
13.3 Elimination Reactions in Halogenoalkanes question n answered graded A+ 2023
- Exam (elaborations) • 5 pages • 2023
-
- $12.99
- + learn more
13.3 Elimination Reactions in HalogenoalkanesHow do halogenoalkanes typically react? By nucleophilic substitution How do halogenoalkanes react under different conditions? By elimination How does elimination reactions occur? A hydrogen halide is eliminated from the molecule, leaving a double bond in its place so that an alkene is formed What is the OH- ion from aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide? A nucleophile and its lone pair will attack a halogenoalkane at C

Do you wonder why so many students wear nice clothes, have money to spare and enjoy tons of free time? Well, they sell on Stuvia! Imagine your study notes being downloaded a dozen times for $15 each. Every. Single. Day. Discover all about earning on Stuvia


