Lec Brain Anatomy 2
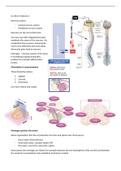
Nervous system:
- Central nervous system
- Peripheral nervous system
Neurons are the unit of the brain.
You have also ODC (oligodendrocytes);
myelinate the axons of the neurons. Via
myelination the neurons communicate
much more efficiently with each other.
Astrocytes gives food to neurons.
Microglia -> immune system of the brain.
If something is going wrong they
produce for example inflammatory
factors.
Orientation in neuroanatomy
Three dissection planes:
1. Sagittal
2. Coronal
3. Horizontal
Use more rostral and caudal.
Meninges (protect the brain)
Sheet organization; first line of protection for brain and spinal cord. Three layers:
- Dura mater; thick and hard
- Arachnoid mater; contains liquid (CSF)
- Pia mater; covers the cortex like a glove
Some places the meninges are thicker for example between the two hemispheres (Falx cerebri) and between
the cerebrum (encephalon) and cerebellum (tentorium cerebri).
, Cerebral lobes
Foramen magnum big hole in the cranium
where the spinal cord is.
Brain is divided in two hemispheres and in
different lobes.
- Frontal: action cortex
- Parietal: language and sensory
information
- Temporal: memory
- Occipital: visuo-spatial processing
Brain has wrinkle appearance. This gives
rise to important structures; gyri and
sulci.
Each lobe has different gyri and sulci.
Which are all connected to the function.
Frontal lobe for example has: superior,
middle and inferior frontal gyrus.
Sulcus centralis (separates the frontal
and parietal lobe) and sulcus lateralis
(difference the frontal and temporal
lobe) are important.
Cortex is really much evolved in humans. Connected with cortex and thinking.
- Gray matter: cell bodies of neurons
- White matter: connecting part between brain regions, axons. ODC
and myelin
Three categories of fibers in the white matter:
- Association fibers: connect different gyri together.
Nervous system:
- Central nervous system
- Peripheral nervous system
Neurons are the unit of the brain.
You have also ODC (oligodendrocytes);
myelinate the axons of the neurons. Via
myelination the neurons communicate
much more efficiently with each other.
Astrocytes gives food to neurons.
Microglia -> immune system of the brain.
If something is going wrong they
produce for example inflammatory
factors.
Orientation in neuroanatomy
Three dissection planes:
1. Sagittal
2. Coronal
3. Horizontal
Use more rostral and caudal.
Meninges (protect the brain)
Sheet organization; first line of protection for brain and spinal cord. Three layers:
- Dura mater; thick and hard
- Arachnoid mater; contains liquid (CSF)
- Pia mater; covers the cortex like a glove
Some places the meninges are thicker for example between the two hemispheres (Falx cerebri) and between
the cerebrum (encephalon) and cerebellum (tentorium cerebri).
, Cerebral lobes
Foramen magnum big hole in the cranium
where the spinal cord is.
Brain is divided in two hemispheres and in
different lobes.
- Frontal: action cortex
- Parietal: language and sensory
information
- Temporal: memory
- Occipital: visuo-spatial processing
Brain has wrinkle appearance. This gives
rise to important structures; gyri and
sulci.
Each lobe has different gyri and sulci.
Which are all connected to the function.
Frontal lobe for example has: superior,
middle and inferior frontal gyrus.
Sulcus centralis (separates the frontal
and parietal lobe) and sulcus lateralis
(difference the frontal and temporal
lobe) are important.
Cortex is really much evolved in humans. Connected with cortex and thinking.
- Gray matter: cell bodies of neurons
- White matter: connecting part between brain regions, axons. ODC
and myelin
Three categories of fibers in the white matter:
- Association fibers: connect different gyri together.