The senses
You can name the receptor for the different senses (sight, taste, smell and hearing).
You can explain how the sensation is translated to an action potential.
You know the structure of the retina and you can explain how light is translated to
neurotransmission.
You can explain how the middle ear and cochlea work and how sound is translated to action
potentials.
You can explain how smells are detected by the brain.
You can name the different receptors for taste and how these trigger an action potential.
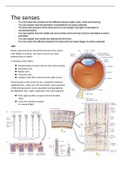
Sight
Retina, neuronal tissue, directly formed out of the neural
tube. Bilayer in embryo. One layer neurons one layer
pigment place in adults.
5 cell types of the retina;
Photoreceptors (cones (colours) and rods (contrast)
Horizontal cells
Bipolar cells
Amacrine cells
Ganglion cells (their axons form the optic nerve)
Photoreceptors cells on the far site, completely embed in
epithelial layer, make sure cells stay health, outer segments
of the photoreceptors can be separated and degraded by
the epithelial layer. Light is detected in the outer segment:
Rods; light sensitive receptors black and white
vision
Cone: less sensitive receptor
for coloured light
, Light hyperpolarises the receptor. In the dark rod
is continuously active. When light rod will stop
firing action potentials. Reduced cGMP levels.
Therefore when you have adapt to dark cause
takes awhile before the cGMP has risen again.
Opsin receptor inactivates the Na+/Ca2+ channel
when exposed to light. Retinal accepts a photon
and activates Opsin. GCPR Opsin activates
transducing. Transducing activates
phosphodiesterase, which hydrolyses cGMP.
cGMP level drops, Ca2+/Na+ channel closes.
Hyperpolarizes in the present of light.
In nature also inotropic receptors of Opsin receptors. Multiple clones of opsin receptors. This will help turn
on or off certain types of neurons with light; optogenetics.
Distribution of cones and rods in the retina.
Best colour vision in fovea (most cones are located, rods hardly present here and more abundant in
lateral sites)
Better light detection in the macula lutea
No sight in the optic disc (exit of optic nerve)
Light is better detected by rods. The surrounding places are more light sensitive; macula lutea. Optic disk is
the blind spot, cause here the optic nerve exit the retina.
You can name the receptor for the different senses (sight, taste, smell and hearing).
You can explain how the sensation is translated to an action potential.
You know the structure of the retina and you can explain how light is translated to
neurotransmission.
You can explain how the middle ear and cochlea work and how sound is translated to action
potentials.
You can explain how smells are detected by the brain.
You can name the different receptors for taste and how these trigger an action potential.
Sight
Retina, neuronal tissue, directly formed out of the neural
tube. Bilayer in embryo. One layer neurons one layer
pigment place in adults.
5 cell types of the retina;
Photoreceptors (cones (colours) and rods (contrast)
Horizontal cells
Bipolar cells
Amacrine cells
Ganglion cells (their axons form the optic nerve)
Photoreceptors cells on the far site, completely embed in
epithelial layer, make sure cells stay health, outer segments
of the photoreceptors can be separated and degraded by
the epithelial layer. Light is detected in the outer segment:
Rods; light sensitive receptors black and white
vision
Cone: less sensitive receptor
for coloured light
, Light hyperpolarises the receptor. In the dark rod
is continuously active. When light rod will stop
firing action potentials. Reduced cGMP levels.
Therefore when you have adapt to dark cause
takes awhile before the cGMP has risen again.
Opsin receptor inactivates the Na+/Ca2+ channel
when exposed to light. Retinal accepts a photon
and activates Opsin. GCPR Opsin activates
transducing. Transducing activates
phosphodiesterase, which hydrolyses cGMP.
cGMP level drops, Ca2+/Na+ channel closes.
Hyperpolarizes in the present of light.
In nature also inotropic receptors of Opsin receptors. Multiple clones of opsin receptors. This will help turn
on or off certain types of neurons with light; optogenetics.
Distribution of cones and rods in the retina.
Best colour vision in fovea (most cones are located, rods hardly present here and more abundant in
lateral sites)
Better light detection in the macula lutea
No sight in the optic disc (exit of optic nerve)
Light is better detected by rods. The surrounding places are more light sensitive; macula lutea. Optic disk is
the blind spot, cause here the optic nerve exit the retina.