Samenvatting
Samenvatting Anatomie 4
- Vak
- Anatomie 4
- Instelling
- Universiteit Antwerpen (UA)
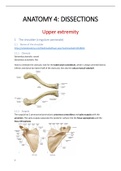
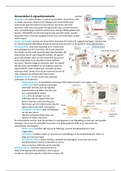
Samenvatting anatomie 4 dissecties van alle leerpaden (in het Engels). Dit document bevat afbeeldingen uit de demovideo's, Acland anatomy video's en overige nuttige afbeeldingen ter verduidelijking. Alle termen die gekend moeten zijn voor het examen, worden besproken.
[Meer zien]