IR | Key points on steroids
Why study IR?
The main reason why we should study IR, is the fact that the entire population of the world is living in
interdependent states.
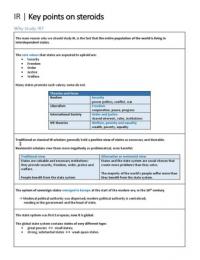
The core values that states are expected to uphold are:
Security
Freedom
Order
Justice
Welfare
Many states promote such values; some do not.
Theories and focus
Realism Security
power politics, conflict, war
Liberalism Freedom
cooperation, peace, progress
International Society Order and justice
shared interests, rules, institutions
IPE theories Welfare, poverty and equality
wealth, poverty, equality
Traditional or classical IR scholars generally hold a positive view of states as necessary and desirable.
↕
Revisionist scholars view them more negatively as problematical, even harmful.
Traditional view Alternative or revisionist view
States are valuable and necessary institutions: States and the state system are social choices that
they provide security, freedom, order, justice and create more problems than they solve.
welfare.
The majority of the world’s people suffer more than
People benefit from the state system they benefit from the state system.
The system of sovereign states emerged in Europe at the start of the modern era, in the 16th century.
Medieval political authority was dispersed; modern political authority is centralized;
residing in the government and the head of state.
The state system was first European; now it is global.
The global state system contains states of very different type:
great powers ↔ small states;
strong, substantial states ↔ weak quasi-states.
,There is a link between the expansion of the state system and the establishment of a world market and a global
economy.
Some developing countries have benefited from integration into the global economy;
others remain poor and undeveloped.
Economic globalization and other developments challenge the sovereign state.
We cannot know for certain whether the state system is now becoming obsolete,
or whether states will find ways of adapting to new challenges.
, IR as an Academic Subject
IR thinking has evolved in stages that are market by specific debates between groups of scholars:
Utopian liberalism (idealism) – the early study of IR vs. Classical realism – the reality of power politics
Traditional approaches vs. behavioralism – revolution towards a science of international politics.
Liberal/realism vs. neo-Marxism
Established traditions vs. new (post-positivist) voices.
The first major debate was won by the realists.
During the Cold War realism became the dominant way of thinking about international relations not only
among scholars but also among politicians, diplomats, and so-called ‘ordinary people’.
Morgenthau’s (1960) summary of realism became the standard introduction to IR in the 1950s and 1960s.
The second major debate is about method.
The contenders are traditionalist and behaviouralists:
Traditionalists: try to understand a complicated social world of human affairs and the values fundamental
to it, such as order, freedom, and justice.
Behaviouralists: find no place for morality or ethics in international theory. Behaviouralism wants to
classify, measure, and explain trough the formulation of general laws like those formulated in the ‘hard’
sciences of chemistry, physics, etc.
The behaviouralists seemed to triumph for a time, but in the end neither side won the debate.
Today both types of method are used in the discipline. There was a revival of traditional normative approaches to
IR after the end of the Cold War.