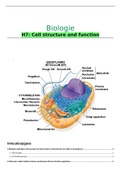
Overview of Inflammation: definitions and general features
Inflammation is a response of vascularized tissues to infections and tissue damage that brings cells
and molecules of host defense from the circulation to the sites where they are needed, to eliminate
the offending agents.
Rid the host both the initial cause of cell injury and the consequences of such injury
Mediators = phagocytic leukocytes, antibodies and complement proteins
Process of inflammation
o The offending agent, which is located in extravascular tissues is recognized by host
cells and molecules
o Leukocytes and plasma proteins are recruited from the circulation to the site where
the offending agent is located
o The leukocytes and proteins are activated and work together to destroy and
eliminate the offending substances
o The reaction is controlled and terminated
o The damaged tissue is repaired
Inflammation may be of two types, acute and chronic
Acute inflammation
o Initial, rapid response
o Exudation of fluid and plasma proteins and emigration of leukocytes
Chronic inflammation
o May follow acute inflammation
o Longer of duration and associated with more tissue destruction, presence of
lymphocytes and macrophages, proliferation of blood vessels and fibrosis
Inflammation is induced by chemical mediators that are produced by host cells in response to
injurious stimuli.
Induce and regulate subsequent inflammatory response
Efflux of plasma and recruitment of circulating leukocytes to the site of offending agent
Activate recruited leukocytes, enhancing ability to destroy and remove offending agents
The external manifestations of inflammation, often called its cardinal signs, are heat (calor), redness
(rubor), swelling (tumor), pain (dolor), and loss of function (function laesa).
Consequences of the vascular changes and leukocyte recruitment and activation
In some situations, the inflammatory reaction becomes the cause of disease, and the damage it
produces is its dominant feature.
Harmful consequences are self-limited and resolve inflammation abates
Inflammatory reaction underlies common chronic diseases
Inflammation is terminated when the offending agent is eliminated.
Reaction resolves because mediators are broken down and dissipated
Anti-inflammatory mechanisms are activated, serving to control the response and prevent it
from causing excessive damage to the host
Process of tissue repair regeneration and scarring
Cause of Inflammation
Infections and microbial toxins
o Acute little or no lasting damage
o Severe systemic reaction fatal
o Prolonged reactions extensive tissue injury
Tissue necrosis
o Ischemia, trauma and physical and chemical injury
Foreign bodies
o May elicit by themselves or they cause traumatic tissue injury
o Endogenous substances in large amounts can cause inflammation
, Immune reactions hypersensitivity
o Autoimmune disease directed against self-antigens
o Allergies against environmental substances
o Stimuli cannot be eliminated persistent and difficult to cure
Recognition of Microbes and Damaged Cells
The first step in inflammatory response is the recognition of microbes and necrotic cells by cellular
receptors and circulating proteins
Cellular receptors for microbes
o Toll-like receptors
Able to detect extracellular and ingested microbes
Recognize motifs common to many microbes PAMPs
Sensors of cell damage
o Cytosolic receptors that recognize molecules that are liberated or altered as a
consequence of cell damage
o Inflammasome
Induces production of cytokine interleukin 1
Recruits leukocytes and induces inflammation
o Autoinflammatory syndromes
Spontaneous inflammation
Circulating proteins
o Complement system
Reacts against microbes and produces mediators of inflammation
o Mannose-binding lectin
Recognizes microbial sugars and promotes ingestion of microbes and
activation of the complement system
o Collectins
Bind to microbes and promote their phagocytosis
Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation has three major components:
1. Dilation of small vessels, leading to increase in blood flow
2. Increased permeability of microvasculature, enabling plasma proteins and leukocytes to
leave circulation
3. Emigration of leukocytes form the microcirculation, their accumulation in the focus of injury
and their activation to eliminate the offending agent
Reactions of Blood Vessels in Acute Inflammation
The vascular reaction of acute inflammation consists of changes in the flow of blood and the
permeability of vessels, both designed to maximize the movement of plasma proteins and leukocytes
out of the circulation and into the site of infection or injury.
Exudate is an extravascular fluid that has a high protein concentration and contains cellular
debris. Presence implies increase in permeability of small blood vessels.
A transudate is a fluid with low protein content, little or on cellular material, and low specific
gravity. Normal permeability
Edema denotes an excess of fluid in the interstitial tissue or serous cavities (exudate or
transudate)
Pus, a purulent exudate, is an inflammatory exudate rich in leukocytes, debris of dead cells
and microbes
Inflammation is a response of vascularized tissues to infections and tissue damage that brings cells
and molecules of host defense from the circulation to the sites where they are needed, to eliminate
the offending agents.
Rid the host both the initial cause of cell injury and the consequences of such injury
Mediators = phagocytic leukocytes, antibodies and complement proteins
Process of inflammation
o The offending agent, which is located in extravascular tissues is recognized by host
cells and molecules
o Leukocytes and plasma proteins are recruited from the circulation to the site where
the offending agent is located
o The leukocytes and proteins are activated and work together to destroy and
eliminate the offending substances
o The reaction is controlled and terminated
o The damaged tissue is repaired
Inflammation may be of two types, acute and chronic
Acute inflammation
o Initial, rapid response
o Exudation of fluid and plasma proteins and emigration of leukocytes
Chronic inflammation
o May follow acute inflammation
o Longer of duration and associated with more tissue destruction, presence of
lymphocytes and macrophages, proliferation of blood vessels and fibrosis
Inflammation is induced by chemical mediators that are produced by host cells in response to
injurious stimuli.
Induce and regulate subsequent inflammatory response
Efflux of plasma and recruitment of circulating leukocytes to the site of offending agent
Activate recruited leukocytes, enhancing ability to destroy and remove offending agents
The external manifestations of inflammation, often called its cardinal signs, are heat (calor), redness
(rubor), swelling (tumor), pain (dolor), and loss of function (function laesa).
Consequences of the vascular changes and leukocyte recruitment and activation
In some situations, the inflammatory reaction becomes the cause of disease, and the damage it
produces is its dominant feature.
Harmful consequences are self-limited and resolve inflammation abates
Inflammatory reaction underlies common chronic diseases
Inflammation is terminated when the offending agent is eliminated.
Reaction resolves because mediators are broken down and dissipated
Anti-inflammatory mechanisms are activated, serving to control the response and prevent it
from causing excessive damage to the host
Process of tissue repair regeneration and scarring
Cause of Inflammation
Infections and microbial toxins
o Acute little or no lasting damage
o Severe systemic reaction fatal
o Prolonged reactions extensive tissue injury
Tissue necrosis
o Ischemia, trauma and physical and chemical injury
Foreign bodies
o May elicit by themselves or they cause traumatic tissue injury
o Endogenous substances in large amounts can cause inflammation
, Immune reactions hypersensitivity
o Autoimmune disease directed against self-antigens
o Allergies against environmental substances
o Stimuli cannot be eliminated persistent and difficult to cure
Recognition of Microbes and Damaged Cells
The first step in inflammatory response is the recognition of microbes and necrotic cells by cellular
receptors and circulating proteins
Cellular receptors for microbes
o Toll-like receptors
Able to detect extracellular and ingested microbes
Recognize motifs common to many microbes PAMPs
Sensors of cell damage
o Cytosolic receptors that recognize molecules that are liberated or altered as a
consequence of cell damage
o Inflammasome
Induces production of cytokine interleukin 1
Recruits leukocytes and induces inflammation
o Autoinflammatory syndromes
Spontaneous inflammation
Circulating proteins
o Complement system
Reacts against microbes and produces mediators of inflammation
o Mannose-binding lectin
Recognizes microbial sugars and promotes ingestion of microbes and
activation of the complement system
o Collectins
Bind to microbes and promote their phagocytosis
Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation has three major components:
1. Dilation of small vessels, leading to increase in blood flow
2. Increased permeability of microvasculature, enabling plasma proteins and leukocytes to
leave circulation
3. Emigration of leukocytes form the microcirculation, their accumulation in the focus of injury
and their activation to eliminate the offending agent
Reactions of Blood Vessels in Acute Inflammation
The vascular reaction of acute inflammation consists of changes in the flow of blood and the
permeability of vessels, both designed to maximize the movement of plasma proteins and leukocytes
out of the circulation and into the site of infection or injury.
Exudate is an extravascular fluid that has a high protein concentration and contains cellular
debris. Presence implies increase in permeability of small blood vessels.
A transudate is a fluid with low protein content, little or on cellular material, and low specific
gravity. Normal permeability
Edema denotes an excess of fluid in the interstitial tissue or serous cavities (exudate or
transudate)
Pus, a purulent exudate, is an inflammatory exudate rich in leukocytes, debris of dead cells
and microbes