Lnatale5264
Op deze pagina vind je alle documenten, voordeelbundels en oefenvragen die worden aangeboden door verkoper lnatale5264.
- 18
- 0
- 3
Community
- Volgers
- Volgend
21 items

Algebra for Calculus- Chapter 5 Notes Bundle
This bundle includes a basic introduction to the notion of inverse functions and how to properly determine when a function is invertible. Then, we examine this topic further by looking at one of the most famous inverse functions in all of algebra: the logarithmic function. The bundle includes an assortment of practice dealing with inverse functions
- Voordeelbundel
- • 3 items •
- 5.1 Inverse Functions • College aantekeningen
- 5.3 Logarithmic Functions and Properties • College aantekeningen
- 5.5 Solving Exponential and Log Equations • College aantekeningen
This bundle includes a basic introduction to the notion of inverse functions and how to properly determine when a function is invertible. Then, we examine this topic further by looking at one of the most famous inverse functions in all of algebra: the logarithmic function. The bundle includes an assortment of practice dealing with inverse functions

5.5 Solving Exponential and Log Equations
After discussing some key features and properties of logarithmic functions, as well as those of exponential functions, it's time to solve some equations involving logs and exponents. This section focuses on developing strong algebraic techniques for solving equations dealing with logs and exponents, emphasizing what's called the "uniqueness property" and how that principle helps us with the problem-solving
- Voordeelbundel
- College aantekeningen
- • 3 pagina's •
After discussing some key features and properties of logarithmic functions, as well as those of exponential functions, it's time to solve some equations involving logs and exponents. This section focuses on developing strong algebraic techniques for solving equations dealing with logs and exponents, emphasizing what's called the "uniqueness property" and how that principle helps us with the problem-solving
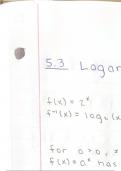
5.3 Logarithmic Functions and Properties
After learning about the notion of inverse functions, we now turn to one of the most important functions in algebra: the logarithmic function. It turns out that the logarithmic function is the inverse of the exponential function, and logs come with their own set of unique properties. We discuss the key features and special properties of logs in this section, along with how to properly define the domain of the log.
- Voordeelbundel
- College aantekeningen
- • 4 pagina's •
After learning about the notion of inverse functions, we now turn to one of the most important functions in algebra: the logarithmic function. It turns out that the logarithmic function is the inverse of the exponential function, and logs come with their own set of unique properties. We discuss the key features and special properties of logs in this section, along with how to properly define the domain of the log.

5.1 Inverse Functions
Some mathematical functions possess a special property known as being "invertible." In other words, these functions have a unique inverse function if they are "one-to-one." In this section, we discuss what it means for a function to be one-to-one and why inverse functions matter. We learn an algebraic method of determining inverse functions given the original parent functions, as well as how to identify key features of this new function we're dealing with.
- Voordeelbundel
- College aantekeningen
- • 4 pagina's •
Some mathematical functions possess a special property known as being "invertible." In other words, these functions have a unique inverse function if they are "one-to-one." In this section, we discuss what it means for a function to be one-to-one and why inverse functions matter. We learn an algebraic method of determining inverse functions given the original parent functions, as well as how to identify key features of this new function we're dealing with.

4.4 Zeros of Polynomials
A "zero" of a polynomial is a value that makes the whole polynomial equal to zero. These values are also called roots, solutions, or x-intercepts. In these notes, we discuss a variety of methods on how to find the zeros of any given polynomial equation. We learn about a couple essential theorems used in the process of determining a polynomial's zeros and the type of information these tests reveal in different situations.
- College aantekeningen
- • 7 pagina's •
A "zero" of a polynomial is a value that makes the whole polynomial equal to zero. These values are also called roots, solutions, or x-intercepts. In these notes, we discuss a variety of methods on how to find the zeros of any given polynomial equation. We learn about a couple essential theorems used in the process of determining a polynomial's zeros and the type of information these tests reveal in different situations.

4.3 Polynomial Division, Remainder Theorem, and Factor Theorem
Polynomial division is the process by which you divide one polynomial by another. Similar to how you divide numbers, you will be left with a quotient polynomial and a remainder polynomial. These notes discuss the methods of long division and synthetic division to find the solutions/factors of any given polynomial. In addition, we discuss the importance of the quotient polynomial and the remainder polynomial in what's called the "Remainder Theorem."
- College aantekeningen
- • 4 pagina's •
Polynomial division is the process by which you divide one polynomial by another. Similar to how you divide numbers, you will be left with a quotient polynomial and a remainder polynomial. These notes discuss the methods of long division and synthetic division to find the solutions/factors of any given polynomial. In addition, we discuss the importance of the quotient polynomial and the remainder polynomial in what's called the "Remainder Theorem."
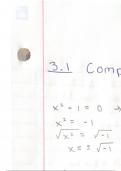
Algebra for Calculus- Chapter 3 Notes Bundle
This bundle includes class notes from a major section in Algebra for Calculus- that is, how to solve and graph major types of functions and equations that serve as a foundation for calculus. Topics in this bundle include complex numbers, quadratic functions/equations, rational equations, radical equations, and absolute value equations/inequalities.
- Voordeelbundel
- • 5 items •
- 3.1 Complex Numbers • College aantekeningen
- 3.2 Quadratic Functions, Quadratic Equations, Solutions, Zeros, and x-Intercepts • College aantekeningen
- 3.3 Analyzing Graphs of Quadratic Functions • College aantekeningen
- 3.4 Solving Rational and Radical Equations • College aantekeningen
- 3.5 Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities • College aantekeningen
This bundle includes class notes from a major section in Algebra for Calculus- that is, how to solve and graph major types of functions and equations that serve as a foundation for calculus. Topics in this bundle include complex numbers, quadratic functions/equations, rational equations, radical equations, and absolute value equations/inequalities.

3.5 Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
When solving an equation or inequality containing an absolute value, you must consider both the positive and negative values that could produce the same absolute value. Essentially, you need to solve for both the positive and negative versions of the expression in order to determine all possible solutions. In these notes, we practice solving absolute value equations and inequalities in a number of examples to properly determine all the solutions to our problem.
- Voordeelbundel
- College aantekeningen
- • 3 pagina's •
When solving an equation or inequality containing an absolute value, you must consider both the positive and negative values that could produce the same absolute value. Essentially, you need to solve for both the positive and negative versions of the expression in order to determine all possible solutions. In these notes, we practice solving absolute value equations and inequalities in a number of examples to properly determine all the solutions to our problem.
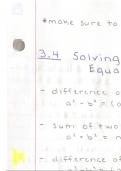
3.4 Solving Rational and Radical Equations
In this section, we learn how to solve for x given two types of equations: rational equations and radical equations. We learn about what's called an "extraneous root" and how to properly check our final solutions. Additionally, we learn how to factor a difference of two cubes or a sum of two cubes to help us identify our roots.
- Voordeelbundel
- College aantekeningen
- • 4 pagina's •
In this section, we learn how to solve for x given two types of equations: rational equations and radical equations. We learn about what's called an "extraneous root" and how to properly check our final solutions. Additionally, we learn how to factor a difference of two cubes or a sum of two cubes to help us identify our roots.

3.3 Analyzing Graphs of Quadratic Functions
In this section, we further examine quadratic functions by analyzing their U-shaped graphs. Key features to identify on a quadratic's graph include the vertex, axis of symmetry, end behavior, x- and y-intercepts, and concavity. Given a quadratic equation in standard form, these notes guide you through the proper steps on how to properly sketch the graph of the function, thoroughly identify each key feature, and rewrite the equation in shifted/vertex form as well.
- Voordeelbundel
- College aantekeningen
- • 5 pagina's •
In this section, we further examine quadratic functions by analyzing their U-shaped graphs. Key features to identify on a quadratic's graph include the vertex, axis of symmetry, end behavior, x- and y-intercepts, and concavity. Given a quadratic equation in standard form, these notes guide you through the proper steps on how to properly sketch the graph of the function, thoroughly identify each key feature, and rewrite the equation in shifted/vertex form as well.
