Understand the role of hormones in the
regulation and control of
the reproductive system
P3 - DESCRIBE THE STRUCTURE AND
FUNCTION OF REPRODUCTIVE
ANATOMY
The reproductive system is a system within the body that is responsible for
sexual reproduction as well as many other functions. Both the female and
male reproductive system have differences in their requirements and
functions as well as the organs involved. Below will be a discussion of both
the female and male reproductive system with the aid of a visual labelled
diagram and the functions of each of the components labelled in both
genders.
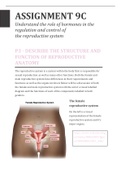
The female
reproductive system
On the left is a visual
representation of the female
reproductive system and it’s
major organs.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.g
ov/books/NBK65829/figur
e/CDR0000062903__286/
,The Fallopian tube
The Fallopian tube acts as a bridge/connection between the ovaries and the
uterus and is located underneath the abdomen and pelvis area. They have a
tube like structure and are known to be muscular as well as being lined with
columnar epithelial cells. The structure of the Fallopian tubes are split into 3
fragments. The first fragment is referred to as the isthmus which is the most
nearest to the ovaries whereas the ampulla which is the second fragment is
the place where the process of fertilization normally is conducted in. The
fragment which is the most distanced from the uterus is know as the
infundibulum. All of these structures above aid in functions which the
Fallopian tube is responsible for carrying out. For example functions such as
the transportation/movement of the ova released from the ovaries to be
transported to the uterus. In terms of the process of fertilisation the
Fallopian tube plays a significant role in this by transporting the male
material which is known as sperm to the cell for fertilisation to be
undertaken.
Ovaries
This structure is considered to be a gland and are attached to the Fallopian
tubes located in the ovarian fossae with a round structure. The structure and
size of this component is often referred to as an almond meaning it is small in
size and oval in terms of shape. It is approximately 3.5 cm in length. They are
responsible for being the production site of the ova and also play a role in
fertilisation since the egg being fertilised is produced at this site. Until
potential fertilisation can occur the ovaries act as protection for the eggs of
the female. Additionally The eggs are released each month which causes the
initiation of the menstruation cycle.
2
, Uterus
The third component is known as the uterus which is located in between the
rectum and the bladder with a muscular structure similar to that of the
Fallopian tubes in contrast to the almond structure of the ovaries the uterus
is considered to be pear shaped. The uterus has 3 main fragments known as
the fundus, the body and the cervix. The uterus wall is compromised of a a
layer known as the myometrium which is also known to be the thickest layer
in comparison to the other layers and has a smooth muscular structure. The
first fragment of the uterus known as the fundus is the very top of the uterus
and has the responsibility in carrying out the function of acting as a location
where the fertilised embryo will stay while this develops into a fetus.
Whereas the second fragment called the body is responsible for acting as the
source of nourishment for the fetus while it is still developing. The cervix is
known as the main entrance for the acceptance of male sperm in order to
move through to fertilise the egg as well as the production of cervical mucus
which acts as aid for the sperm to to enter the uterus. The dilation of the
uterus happens in order to prepare are initiate labour so that the baby can
easily be pushed out as a result of the dilation.
Endometrium
The endometrium is located within the uterus acting as a inside layer of
lining. However in terms of structural features the endometrium also
contains sub layers within it known as the stratum, stratum spongiosum and
compactum. In terms of the composition of endometrium it contains vascular
smooth muscle cells as well as luminal epithelium. The endometrium plays a
massive function in mensuration and pregnancy as each month this lining
thickens in preparation for potential pregnancy. The shedding of the
endometrium occurs hence causing the process of menstruation when there
is no possibility for pregnancy to occur.
3