Calorimetry
As part of my role as a new technician at an independent materials science company, I was required to carry out the
calibration of thermometers. This is because poor calibration of the thermometers would lead to imprecise and
unreliable data. Calibration is defined as comparing the measurement of a device in order to determine its
accuracy.
I will also be collecting data to construct a cooling curve for paraffin wax and stearic acid. Cooling curves are used by
scientists to determine the temperature changes that occur as a substance cools down. One can determine the
temperature at which a phase change happens by looking at the rate of cooling. This can be calculated from the
cooling curve graphs by calculating the gradient of each point. The rate of cooling shows how long it takes for a
substance to reach a certain temperature and become a certain state of matter.
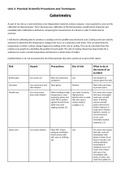
Outlined below is my risk assessment for all of the practicals that were carried out as part of this report.
Risk Hazard Precautions Size of risk What to do in
the event of an
accident
Broken glass Can cause cuts Wear eye protection Low Use tweezers to
and gloves remove glass from skin
Hot water Can cause burns and Wear gloves Medium Wash with cold water
skin irritation to prevent burns
Paraffin wax Can cause severe When handling at high Low order of toxicity. If it comes into contact
burns and irritation temperatures, wear High-pressure with eyes, thoroughly
protective gloves and injection into or under wash eyes out with
other PPE to protect skin may cause a water. If inhaled,
against thermal burns. serious medical remove yourself
Spills may cause condition. [1] and/or others from
slipping hazards. [1] further exposure. If
respiratory irritation,
dizziness, nausea, or
unconsciousness
occurs, seek
immediate medical
assistance. [1]
Stearic acid Can cause irritation Wear PPE. Ensure Low If it comes into contact
adequate ventilation. with skin, wash off
Avoid contact with immediately with
skin, eyes or clothing. plenty of water for at
[2] least 15 minutes. Get
medical attention
immediately if
symptoms occur. If it
comes into contact
with eyes, rinse
immediately with
plenty of water, also
under the eyelids, for
,Unit 2: Practical Scientific Procedures and Techniques
at least 15 minutes.
Get medical attention.
[2]
Calibration of liquid-filled thermometers and digital
thermometers:
Before I carried out my experiments, I tested two types of thermometers (liquid-filled and digital) using ice and
water at 0°C and 100°C to calibrate them and check if the readings would be accurate. I did this to prevent errors
that may occur when readings are being taken. Outlined below is the method that I used, which details how I
calibrated the thermometers appropriately.
Equipment
● Liquid-filled thermometer
● Digital thermometer
● Beaker
● Ice cubes
● Kettle
● Stopwatch
Method- Melting point
1. Fill a beaker with 2-3 ice cubes and top up with a small amount of water.
2. Allow this to sit for approximately 3 minutes.
3. Gently stir with a thermometer for 1 minute. Ensure that the thermometer does not touch the sides or base
of the beaker.
4. Record the temperature. The temperature should be 0°C.
5. Repeat steps 1-4 three times and record these results in a table. Calculate an average temperature.
Method- Boiling point
1. Fill a beaker with boiling water from a kettle.
2. Place a thermometer into the beaker for 1 minute, ensuring that it does not touch the sides or base of the
beaker.
3. Record the temperature. The temperature should be 100°C.
4. Repeat steps 1-2 three times and record these results in a table. Calculate an average temperature.
Results:
MELTING POINT
Digital thermometer
Attempt Temperature (°C)
1 8
2 8.5
, Unit 2: Practical Scientific Procedures and Techniques
3 10
Average 8.8
Liquid-filled thermometer
Attempt Temperature (°C)
1 4.7
2 7.2
3 7.8
Average 6.6
BOILING POINT
Digital thermometer
Attempt Temperature (°C)
1 83
2 78
3 76
Average 79
Liquid-filled thermometer
Attempt Temperature (°C)
1 77
2 80
3 82
Average 79.7
Evaluation
As observed in my findings, we can conclude that these thermometers are not calibrated properly. For both the
melting and boiling points, the average temperatures tend to be slightly different than the values they should be at.
I think that this may have happened because I did not leave the thermometer inside the beaker for long enough for
it to adjust to the water temperature. To collect data of a better quality, I ensured that the boiling water is still at its
high temperature rather than waiting for quite a while to start the experiment. For some attempts, I got distracted
by my surroundings and accidentally allowed the thermometer to touch the bottom of the beaker. This was a
problem because it affected the reading on the thermometer, therefore affecting the results. To prevent this from
happening, I would make sure to observe the thermometer at all times in order to guarantee results of greater
accuracy. Another thing that I found was that it took longer for the thermometer to adjust to the boiling water than
the ice water. As it took a while to adjust, this reduced the time that we had to calibrate both thermometers for
both the melting and boiling point. I came to the conclusion that the liquid-filled thermometer was the most