Lecture notes
HR (Human Reproduction) Preparation for Birth and Delivery
- Module
- Medicine (A100)
- Institution
- Cambridge University (CAM)
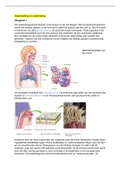
University of Cambridge (Medicine 1st class): Summary of key points of HR (Human Reproduction) Preparation for Birth and Delivery lectures for 2nd year.
[Show more]