Notes:
The traditional PM’s role:
• Responsibility: planning, to the business/client
• Control: schedule, budget, estimates, resources
• Authority: for everything
This causes problems for the PM:
• Responsibility – does the PM know how to code? How can the PM plan the coding?
• Control – schedule always slipping, extending budgets, growing/receding staff list, hopeless
estimates
• Authority for everything and culpability for all mistakes, delays, bugs
Team in Scrum:
• Traditionally, the project manager tells the team what to do and manages its work.
• In Scrum, however, the team selects the work that it will do.
Scrum Team Roles:
Product Owner:
• Is typically a project's key stakeholder.
• Maintains, updates, administers, and ranks the product backlog (user stories).
• Collaborates with the team to define the objectives of each sprint.
• Answers questions of the requirements from the team.
• Ranks/prioritizes the user stories.
Scrum Master:
• ScrumMaster provides leadership, guidance, and coaching during the Scrum project.
• Ensures the team is highly performing.
• Removes Impediments to the team.
• Ensures Product Owner has performed their work.
• Usually is part of the Team.
The Team:
• Estimate the tasks.
• Choose the tasks to be developed.
Team Responsibilities:
• The team looks at the requirements, considers the available technology and evaluates its
own skills and capabilities.
• For each iteration, they collectively determine how to build the functionality, modifying its
approach daily as it encounters new complexities, difficulties, and surprises.
• The team figures out what needs to be done and selects the best way to do it.
,Why Plan in Agile?
We don't plan so we can predict the future. We plan because:
• We need to ensure that we are always working on the most important thing we need to do.
• We need to coordinate with other people.
• When unexpected events occur, we need to understand the consequences for the first two.
What do Plans include?
• Milestones
• Events
• The consequences of the inevitable changes.
Decisions in Agile Approaches:
• Business decisions in planning are
o Dates
o Scope
o Priority
• Technical decisions in planning are:
o Estimates
Controlling a Project: Four Variables:
• Cost
o People
o Tools
o Motivation
o Overtime
• Quality
o External Quality: One perceived by the customer
▪ Bugs
▪ Non-functional requirements: include these in the scope of the project.
o Internal quality: the design, tests
• Time & Scope: If you add scope or change it that will impact on the time.
Traditional Planning:
• Feasibility study - decide if a project is worth doing
• Plan how you are going to do it, then do it
Agile Projects: Characteristics:
• Short iterations.
• Collaborating in teams.
• Small unit of work: increments
• Responding to change.
• Ongoing planning and measurement.
• Early and Continuous testing.
• Early and Frequent delivery.
• Simplified communication.
, • Co-location.
Agile Manifesto:
• Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
• Working software over comprehensive documentation
• Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
• Responding to change over following a plan
Project Breakdown in Agile:
An Iteration:
• They are timeboxed. Never extended
• Fixed length. For example, 2 or 4 weeks
• Each iteration has the same construction
Start > Realize > Evaluate
Product Items vs Iteration Items:
• The list of all work items is often called the project or product backlog.
• The list of work items selected in each iteration is called iteration backlog.
Estimate Work Items:
• Expressed in Story Points.
o Story Points are relative to size and effort of work items.
Story Points:
• Are Relative Values.
Factors to consider:
• The amount of work to do
• Complexity
• Risk and Uncertainty
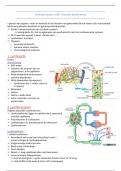
Scrum Process:
• Scrum is an iterative and incremental process.
• Iteration (Sprint): Activities of realization.
• Increment: Shippable output of an iteration.
• Inspection: On a daily basis, the team review and inspect each other's activities and perform
adaptations.
• Product Backlog: The list of requirements that drive the project.
,
The traditional PM’s role:
• Responsibility: planning, to the business/client
• Control: schedule, budget, estimates, resources
• Authority: for everything
This causes problems for the PM:
• Responsibility – does the PM know how to code? How can the PM plan the coding?
• Control – schedule always slipping, extending budgets, growing/receding staff list, hopeless
estimates
• Authority for everything and culpability for all mistakes, delays, bugs
Team in Scrum:
• Traditionally, the project manager tells the team what to do and manages its work.
• In Scrum, however, the team selects the work that it will do.
Scrum Team Roles:
Product Owner:
• Is typically a project's key stakeholder.
• Maintains, updates, administers, and ranks the product backlog (user stories).
• Collaborates with the team to define the objectives of each sprint.
• Answers questions of the requirements from the team.
• Ranks/prioritizes the user stories.
Scrum Master:
• ScrumMaster provides leadership, guidance, and coaching during the Scrum project.
• Ensures the team is highly performing.
• Removes Impediments to the team.
• Ensures Product Owner has performed their work.
• Usually is part of the Team.
The Team:
• Estimate the tasks.
• Choose the tasks to be developed.
Team Responsibilities:
• The team looks at the requirements, considers the available technology and evaluates its
own skills and capabilities.
• For each iteration, they collectively determine how to build the functionality, modifying its
approach daily as it encounters new complexities, difficulties, and surprises.
• The team figures out what needs to be done and selects the best way to do it.
,Why Plan in Agile?
We don't plan so we can predict the future. We plan because:
• We need to ensure that we are always working on the most important thing we need to do.
• We need to coordinate with other people.
• When unexpected events occur, we need to understand the consequences for the first two.
What do Plans include?
• Milestones
• Events
• The consequences of the inevitable changes.
Decisions in Agile Approaches:
• Business decisions in planning are
o Dates
o Scope
o Priority
• Technical decisions in planning are:
o Estimates
Controlling a Project: Four Variables:
• Cost
o People
o Tools
o Motivation
o Overtime
• Quality
o External Quality: One perceived by the customer
▪ Bugs
▪ Non-functional requirements: include these in the scope of the project.
o Internal quality: the design, tests
• Time & Scope: If you add scope or change it that will impact on the time.
Traditional Planning:
• Feasibility study - decide if a project is worth doing
• Plan how you are going to do it, then do it
Agile Projects: Characteristics:
• Short iterations.
• Collaborating in teams.
• Small unit of work: increments
• Responding to change.
• Ongoing planning and measurement.
• Early and Continuous testing.
• Early and Frequent delivery.
• Simplified communication.
, • Co-location.
Agile Manifesto:
• Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
• Working software over comprehensive documentation
• Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
• Responding to change over following a plan
Project Breakdown in Agile:
An Iteration:
• They are timeboxed. Never extended
• Fixed length. For example, 2 or 4 weeks
• Each iteration has the same construction
Start > Realize > Evaluate
Product Items vs Iteration Items:
• The list of all work items is often called the project or product backlog.
• The list of work items selected in each iteration is called iteration backlog.
Estimate Work Items:
• Expressed in Story Points.
o Story Points are relative to size and effort of work items.
Story Points:
• Are Relative Values.
Factors to consider:
• The amount of work to do
• Complexity
• Risk and Uncertainty
Scrum Process:
• Scrum is an iterative and incremental process.
• Iteration (Sprint): Activities of realization.
• Increment: Shippable output of an iteration.
• Inspection: On a daily basis, the team review and inspect each other's activities and perform
adaptations.
• Product Backlog: The list of requirements that drive the project.
,